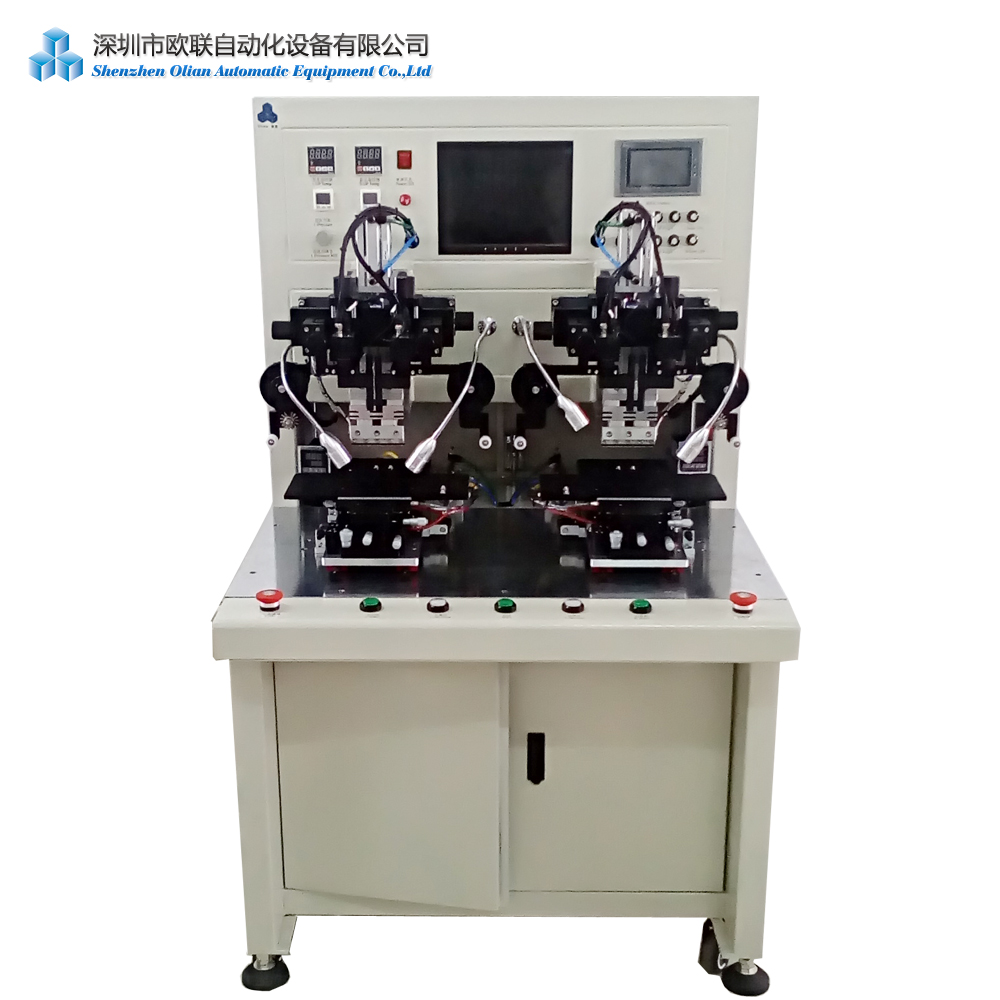

The Bonding Equipment use the ACF tape as the medium ,so it also named ACF bonding equipment /ACF bonding machine.According to different LCD/LED/OLED and different screens, there are many ACF tapes models. ACF tape is the important medium of the ACF bonding process.
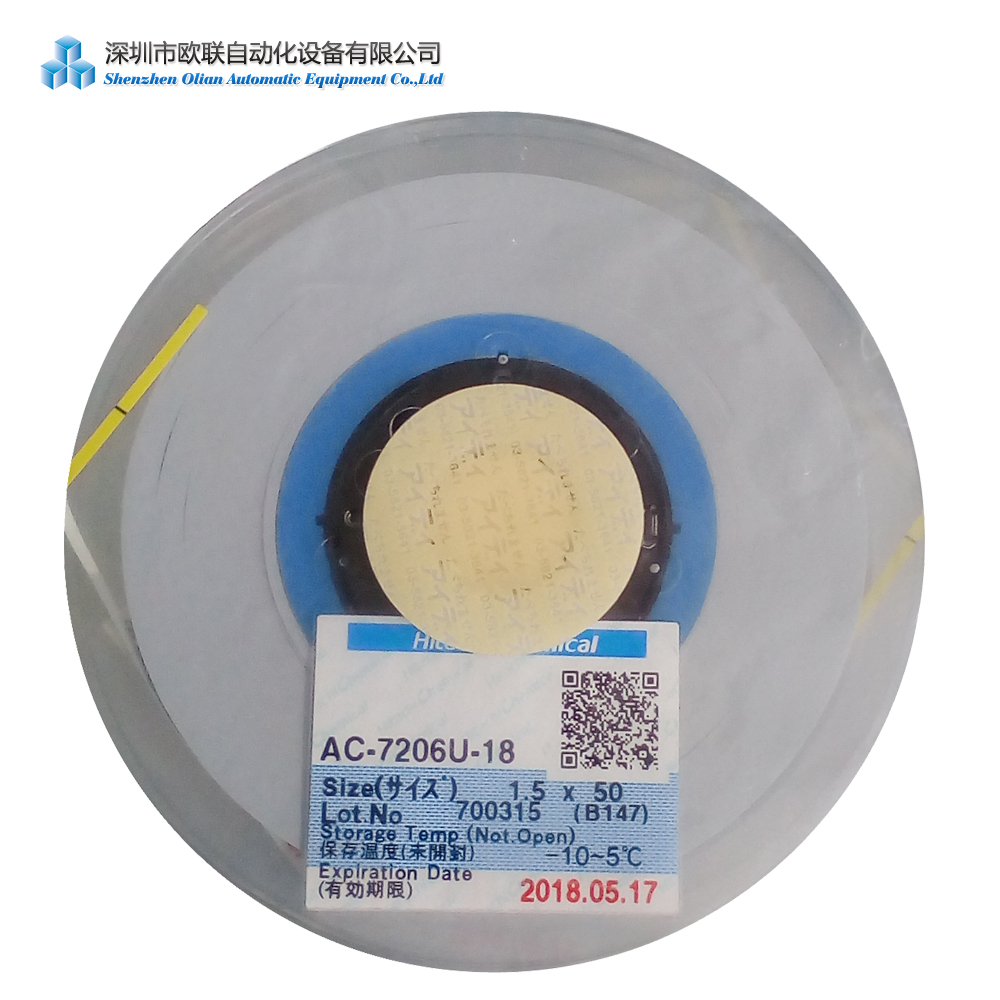
ACF Tape is normally made up of two main components, namely Adhesive & conductive particles.
The adhesive composition is dependent on the materials being assembled. This means an ACF designed for use in a flex-on-glass (FOG) assembly is usually not suitable for use in a chip-on-glass (COG),chip-on-film(COF), flex-on-board(FOB),flex-on-flex(FOF) or any other configurations. It is specific to the application for which it is designed for.
Conductive particles are used to conduct electricity from one side of the bond to the other. Depending on the application, conductive particles range from 3.5μm to 30μm in size, and can be made from Nickel-gold plated polymer spheres, gold plated nickel particles, or lead-free solder materials. Particles may be individually coated with a outer polymer to insulate them from other uncrushed particles, but which will crack open and allow electrical conduction if the particle is trapped and crushed between two pads during assembly.
ACF (Anisotropic conductive film) or ACF tape is an epoxy adhesive system used by electronics industry to make electrical and mechanical connections from drive electronics to substrates.
ACF are filled with conductive particles which provides electrical interconnection between pads through the film thickness (z-direction).
The conductive particles are distributed far apart thus not electrically conductive in the plane direction (X&Y) of the film.
ACF interconnect offers cost savings by substituting conventional mechanical connectors or soldering interconnect.
ACF interconnect allows low height and fine pitch which enables high density and miniaturizing of assembly.
ACF special conductive particle is made from environmental friendly material (ROHs compliance). It provides good metalic bonding.
ACF tape has little conductive particles in the conductive lines of the tape.
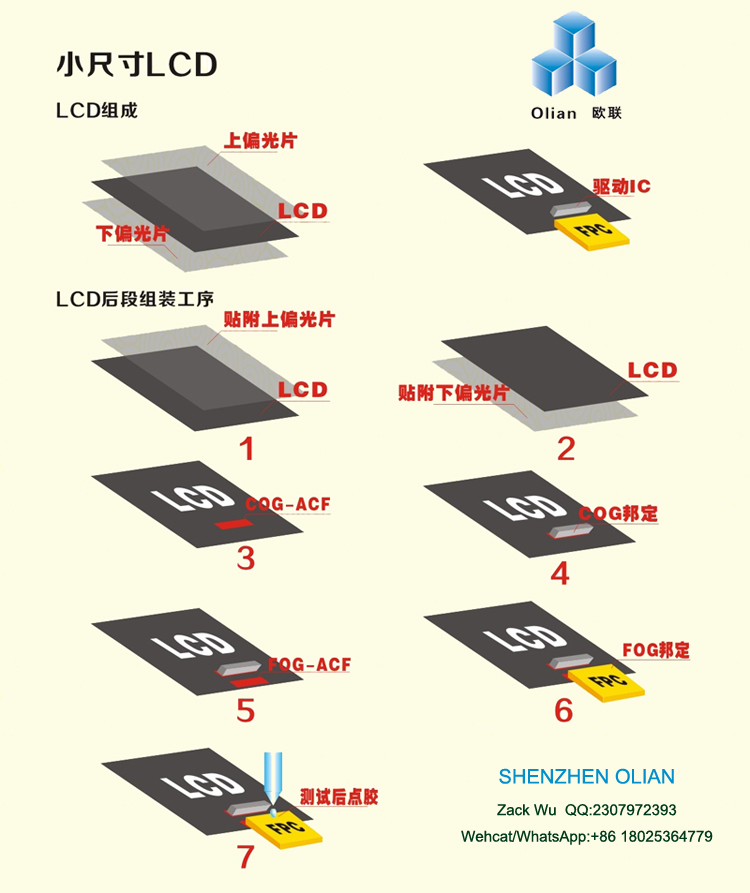
During ACF bonding, a combination of heat & pressure is applied on to chip (FPC/IC) for an appropriate time.
Conductive particles (each 3~30um) are compressed between IC and substrate (glass / PCB) while insulating materials pushed away.
This allows the compressed Ni-Au layer on the particles to conduct electricity between the IC and the substrates (z-axis).
The insulated particles are distributed with a minimum chance of electrical shorting in the x-axis and y-axis.
As the epoxy cures and conductive particles are trapped into permanent compressed form.
The compressed particles, by its elastic nature, are constantly pushing outwards to maintain good electrical conductivity under different environmental conditions.
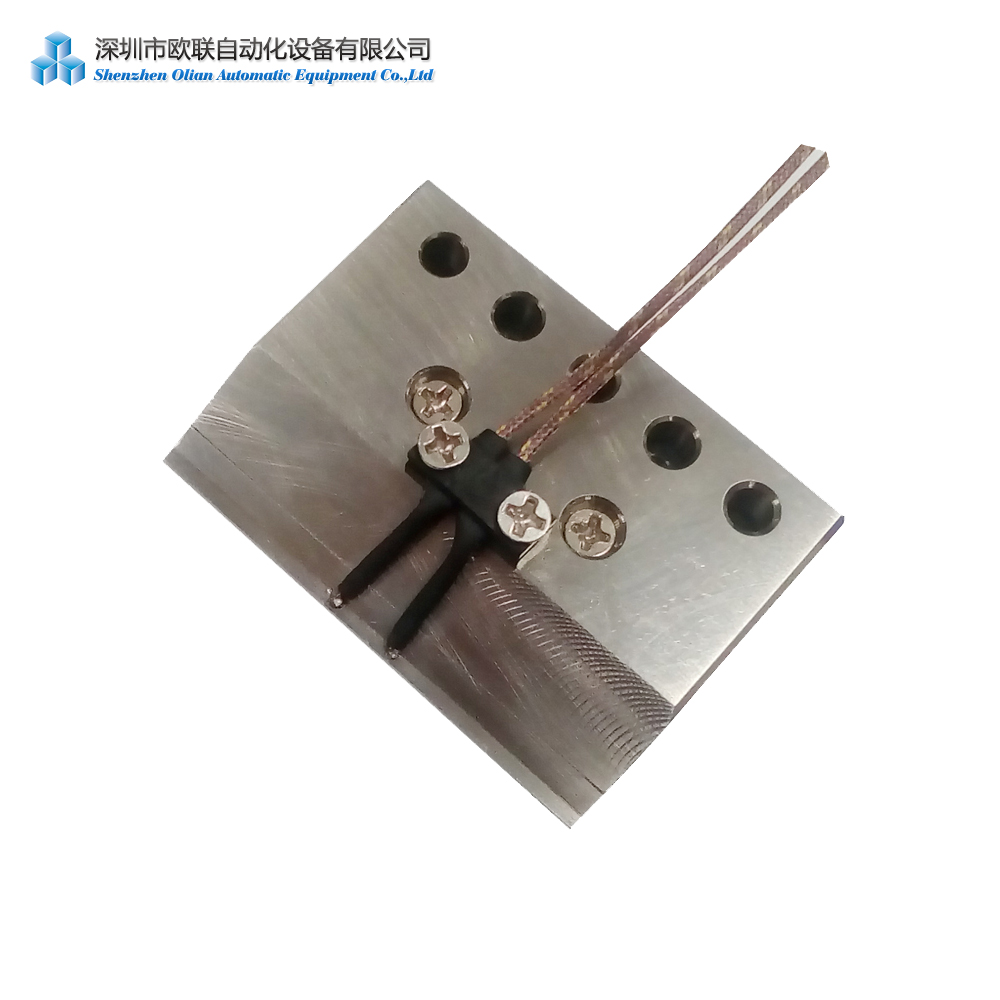
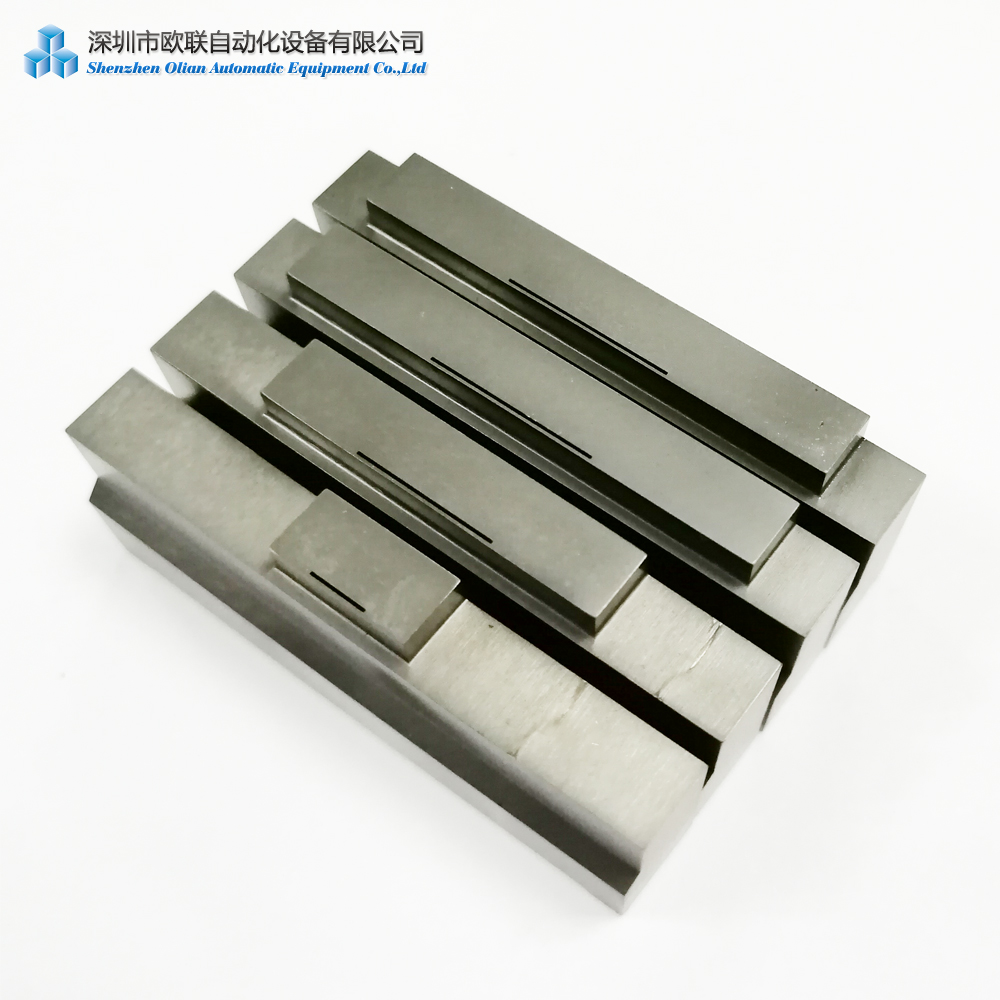

The source for heat and pressure in ACF bonding is most often a hot bar/thermode/bonding head/bonding cutter.
Hot bar bonding systems are designed to heat the hot bar to a specific temperature using low voltage electricity, which temperature is fed back to the controller via a thermocouple.
Tooling is designed to hold the components and position the ACF tape to line up correctly with the conductive pads on the PCB or other component.
The hot bar is then brought into contact with the ACF film over the top of the bonding pad, heated to the bonding temperature, and held for a specified time.
This process is what produces the connection between the ACF tape and the components. Advanced Integrated Technologies is equipped to assist you with your ACF bonding process.
Tell us which products you want to bonding ,then we can suggest you the right ACF bonding equipments for you ..
ACF bonding equipment has been used in glass display applications for many years. It has recently become widely used in COF, COB,COG,FOG,FOB,FOF areas.

Industries that use this technology most are the mobile phone manufacturing, automotive industry, and LCD production, mobile computers, TV manufacturing, open cell panels factories, touch panel ,AD shower, Watch, Pad… factories. and many Labs who researching in the LCD/LED/OLED/MICRO LED/MINI LED displays industries.
Shenzhen olian is a professional ACF bonding equipment design&making factory. Welcome you visit us .
Wechat/whatsapp:+86 18025364779, QQ:2307972393, https://bonding-machine.com
