

Automotive Display Bonding Line
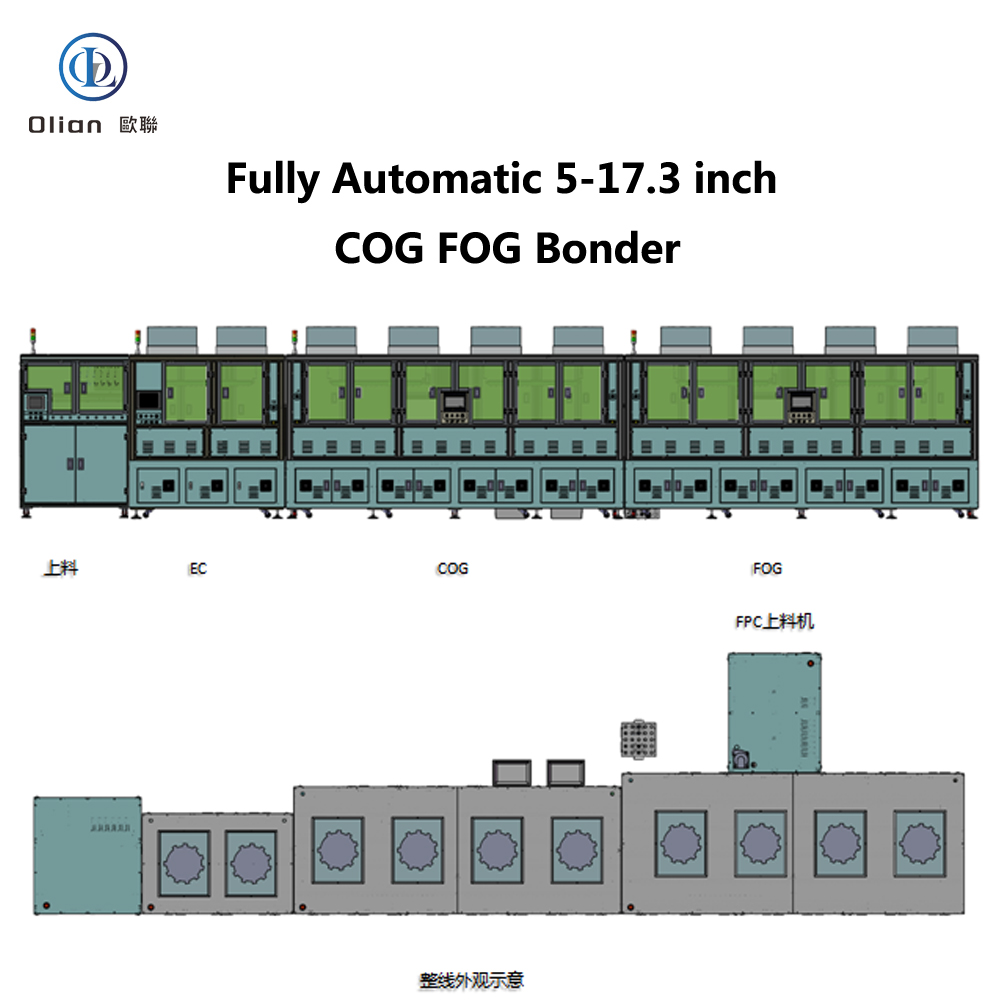
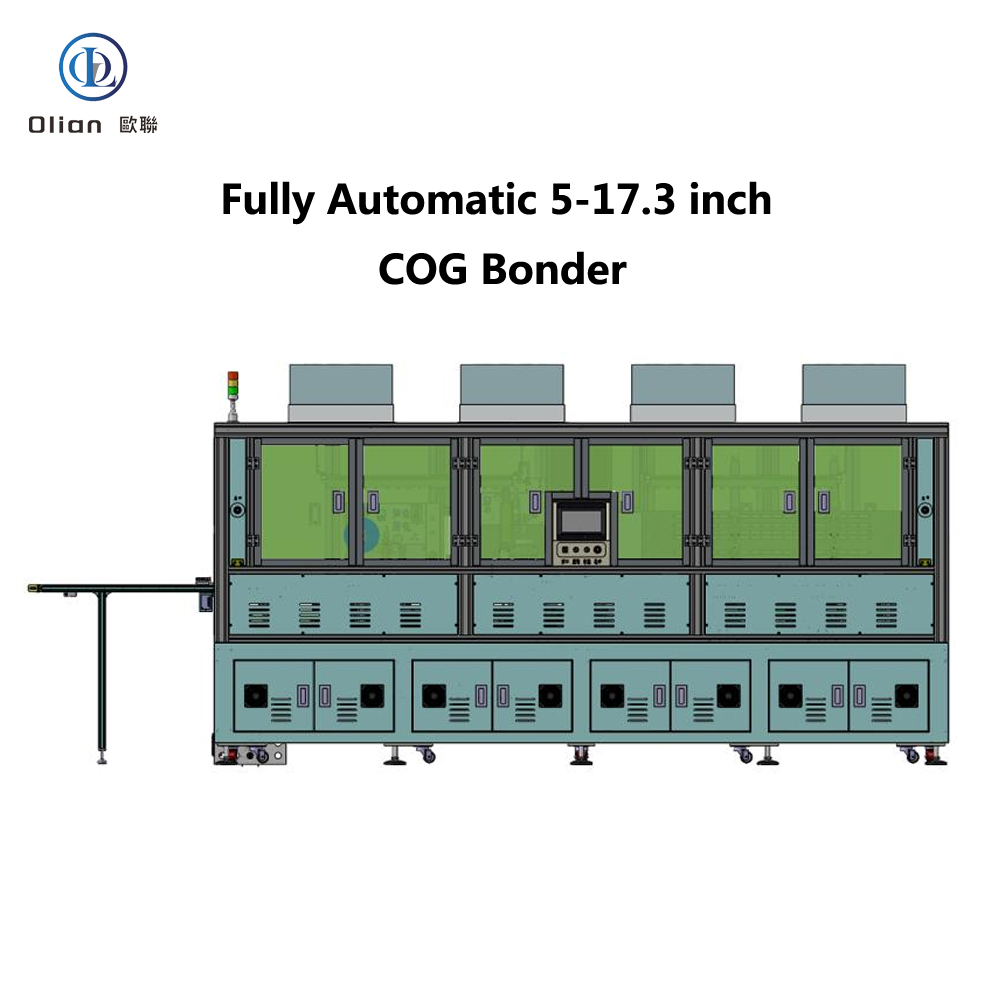



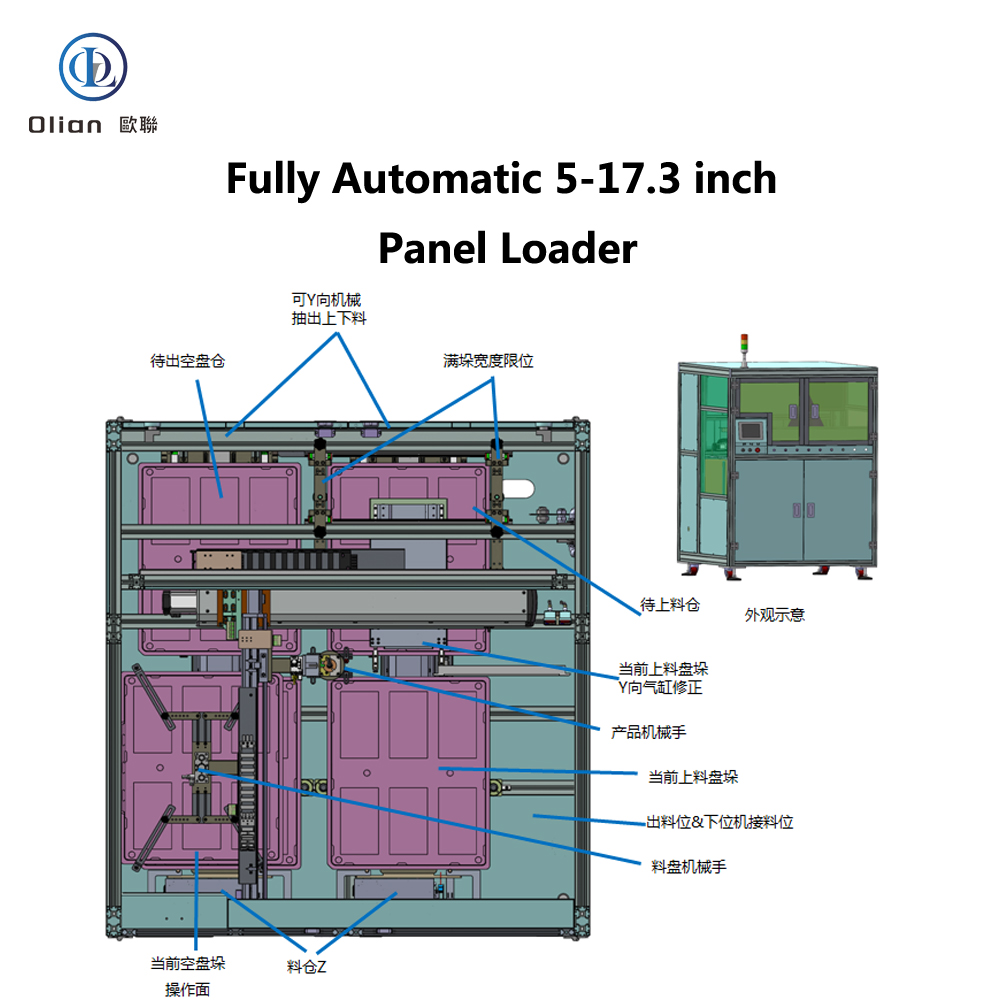
The Automotive Display Bonding Line is a critical and highly specialized segment within the broader automotive display manufacturing process. It refers to the dedicated production stage where key optical and mechanical components of a display—such as the cover glass, touch sensor, display panel (LCD/OLED), and backlight unit—are precisely laminated and bonded together using advanced materials and techniques. This process is essential for ensuring optical clarity, mechanical durability, environmental resistance, and long-term reliability in the harsh operating conditions typical of automotive environments.
As modern vehicles integrate larger, curved, and multi-display consoles, the bonding process has evolved from simple adhesive application to a high-precision, cleanroom-controlled operation involving automated alignment, vacuum lamination, and advanced optically clear adhesives (OCAs) or liquid optical bonding (LOCA). The bonding line plays a pivotal role in determining the final display’s performance, including sunlight readability, touch sensitivity, resistance to delamination, and overall lifespan.
Unlike consumer electronics, automotive displays must endure extreme temperatures (-40°C to +85°C), prolonged UV exposure, high humidity, mechanical vibration, and frequent thermal cycling. The bonding process directly impacts:
● Optical Performance: Minimizing reflections and air gaps to enhance contrast and visibility.
● Mechanical Integrity: Preventing delamination, cracking, or warping over time.
● Touch Sensitivity: Ensuring consistent response by eliminating air pockets between layers.
● Environmental Sealing: Protecting internal components from moisture, dust, and chemical ingress.
● Durability: Meeting automotive-grade reliability standards such as AEC-Q100 and ISO 16750.
The bonding line typically integrates the following components:
● Cover Glass or Lens: Often chemically strengthened (e.g., Gorilla Glass) with anti-reflective (AR), anti-fingerprint (AF), or haptic coatings.
● Touch Sensor Layer: Usually a capacitive touch film (PET or glass-based) with fine conductive patterns.
● Display Panel: LCD or OLED panel with driver ICs and flexible printed circuits (FPCs).
● Optical Clear Adhesive (OCA): A transparent, pressure-sensitive film or liquid adhesive with high refractive index matching.
● Backlight Unit (for LCDs): Includes LED array, light guide plate, and diffusers.
● Bezel and Frame: Provides structural support and alignment during bonding.
A state-of-the-art bonding line consists of the following sequential stages:
● Cleaning and Drying: All substrates are ultrasonically cleaned and dried in a class 100–1000 cleanroom to remove dust, oils, and particulates.
● Plasma Treatment: Surface activation using plasma improves wettability and adhesion, especially for LOCA processes.
● Alignment Mark Detection: Machine vision systems identify alignment markers on each layer for sub-micron precision.
● Layers are temporarily joined under controlled pressure and temperature to ensure initial adhesion without full curing.
● Automated alignment systems (using CCD cameras and servo motors) achieve alignment accuracy within ±5 µm.
● Film OCA Bonding:
○ Pre-cut OCA films are placed between layers.
○ Vacuum laminators apply uniform pressure in a vacuum chamber to eliminate bubbles.
○ Heat may be applied to activate the adhesive.
○ Advantages: Clean, consistent, and suitable for high-volume production.
● Liquid Optical Bonding (LOCA):
○ A liquid adhesive is dispensed around the perimeter of the display.
○ Capillary action draws the adhesive into the gap.
○ UV curing or thermal curing follows under controlled conditions.
○ Advantages: Better for curved or non-uniform gaps; improves impact resistance.
● Thermal Curing: For heat-activated OCAs, displays are passed through convection or IR ovens.
● UV Curing: UV lamps expose the adhesive to initiate polymerization (common in LOCA).
● Curing profiles are precisely controlled to ensure complete cross-linking without damaging sensitive components.
● Debubbling: Additional vacuum or pressure cycles remove any residual micro-bubbles.
● Trimming and Edge Sealing: Excess OCA or cured LOCA is trimmed; edge sealants may be applied to prevent moisture ingress.
● Cleaning and Inspection: Final cleaning with isopropyl alcohol or plasma; visual and automated inspection follows.
● Optical Inspection: Automated vision systems check for bubbles, delamination, dust, and alignment errors.
● Peel Strength Testing: Sample units undergo adhesion tests to verify bond integrity.
● Thermal Shock Testing: Bonded units are cycled between extreme temperatures to detect early failure.
● Humidity Resistance Testing: Units are exposed to high humidity (e.g., 85°C/85% RH) for 1,000+ hours.
The automotive display bonding line is highly automated to ensure consistency and yield:
● Robotic Handling: SCARA or Cartesian robots transfer delicate assemblies without contamination.
● Machine Vision Guidance: Real-time alignment correction ensures micron-level accuracy.
● Environmental Control: Temperature, humidity, and particulate levels are tightly regulated in cleanroom environments (ISO Class 5–6).
● Data Logging and Traceability: Every bonding cycle is recorded (pressure, temperature, time, adhesive type) for quality traceability and process optimization.
Challenges:
● Bonding curved or free-form displays requires custom tooling and flexible adhesives.
● Minimizing voids and bubbles in large-format displays (e.g., 15+ inch screens).
● Managing thermal expansion mismatches between glass, plastic, and metal components.
● Achieving fast cycle times without compromising bond quality.
Innovations:
● Smart Adhesives: Temperature- or light-responsive OCAs with self-healing properties.
● Roll-to-Roll (R2R) Bonding: For flexible OLED displays, enabling continuous processing.
● AI-Powered Defect Prediction: Machine learning models analyze bonding parameters to predict failures.
● Hybrid Bonding: Combining OCA and LOCA for optimal performance in complex geometries.
The bonded displays produced on this line are used in:
● Digital instrument clusters
● Central infotainment systems (CID)
● Head-up displays (HUD)
● Rear-seat entertainment
● Mirror-replacement displays (e.g., digital side mirrors)
● Advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) interfaces
● Mini/Micro-LED Integration: Requires new bonding techniques due to higher thermal loads.
● Augmented Reality (AR) HUDs: Demand ultra-high optical clarity and distortion-free bonding.
● Sustainable Adhesives: Development of recyclable or bio-based OCAs.
● In-Mold Electronics (IME): Bonding displays directly into 3D-shaped surfaces.
The Automotive Display Bonding Line is a cornerstone of modern automotive display manufacturing, combining precision engineering, advanced materials science, and smart automation to deliver displays that are not only visually stunning but also rugged and reliable. As vehicles evolve into mobile digital platforms, the bonding process will continue to innovate, enabling larger, more durable, and more interactive displays that enhance both safety and user experience. Investing in advanced bonding technology is essential for manufacturers aiming to meet the growing demands of the next-generation automotive market.