
A COF bonding machine is the quiet hero inside every ultra-slim TV, foldable phone, and curved automotive cluster. COF means Chip-On-Film: a bare driver IC is bumped, flipped, and bonded to a thin polyimide ribbon that later folds tightly behind the glass. The machine that performs this microscopic wedding must deliver micron-level alignment, single-degree temperature control, and ton-class pressure accuracy—all in under four seconds. Below you will find a dense but readable walk-through of definition, working principle, core parts, applications, specifications, trends, and maintenance keywords such as “COF bonding machine”, “Chip on Film bonder”, “LCD COF repair equipment”, “pulse heat COF machine”, and “4K TV bonding tool”.
A COF bonding machine is a machine that attaches COFs to LCD OLED MINILED MICROLED FPC FFC PCB Ceramic and silicone substrates with ACF tapes. The bond must conduct vertically between bump and copper track yet stay insulated horizontally between neighboring 20 µm traces. When the film later folds behind the panel, the IC sits in the narrow bezel instead of on the glass, enabling edge-to-edge pictures in smartphones, OLED TVs, and 8K monitors. The same machine also reworks defective TV panels by removing the old IC and rebonding a new one, saving hundreds of dollars per screen.
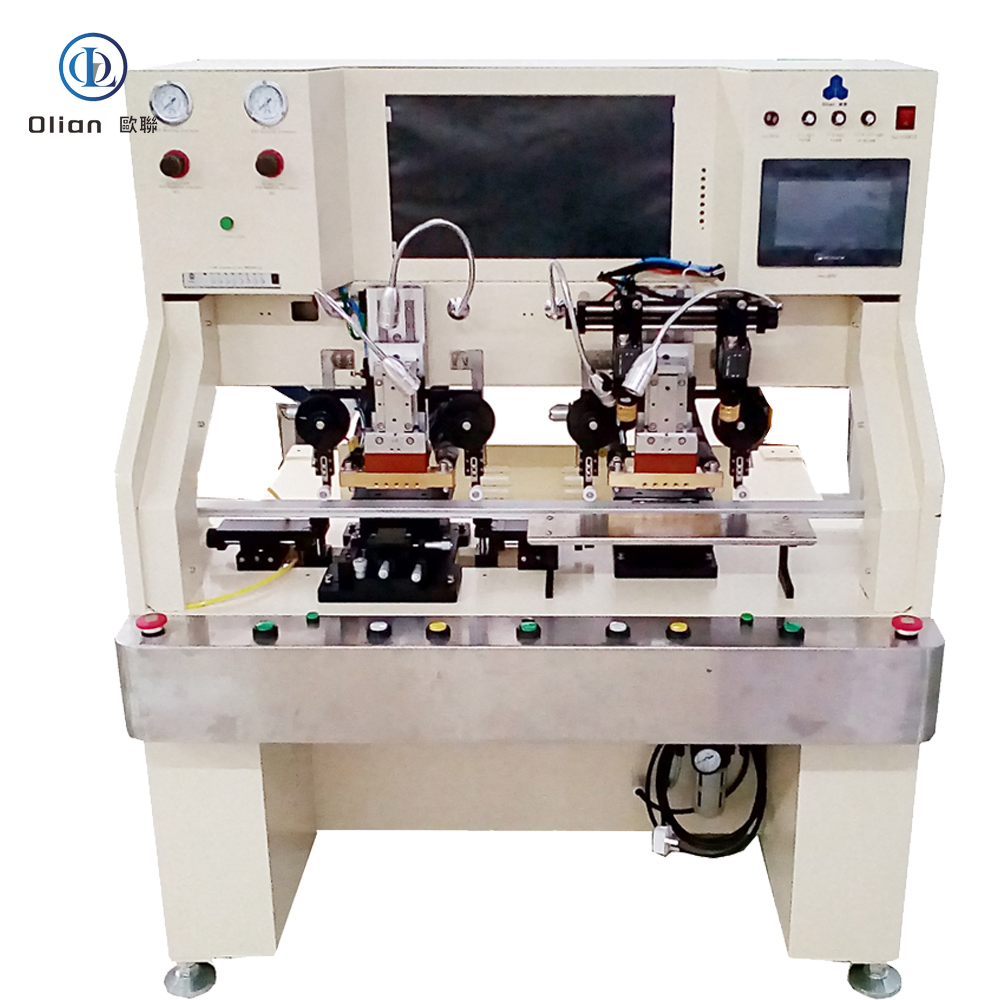
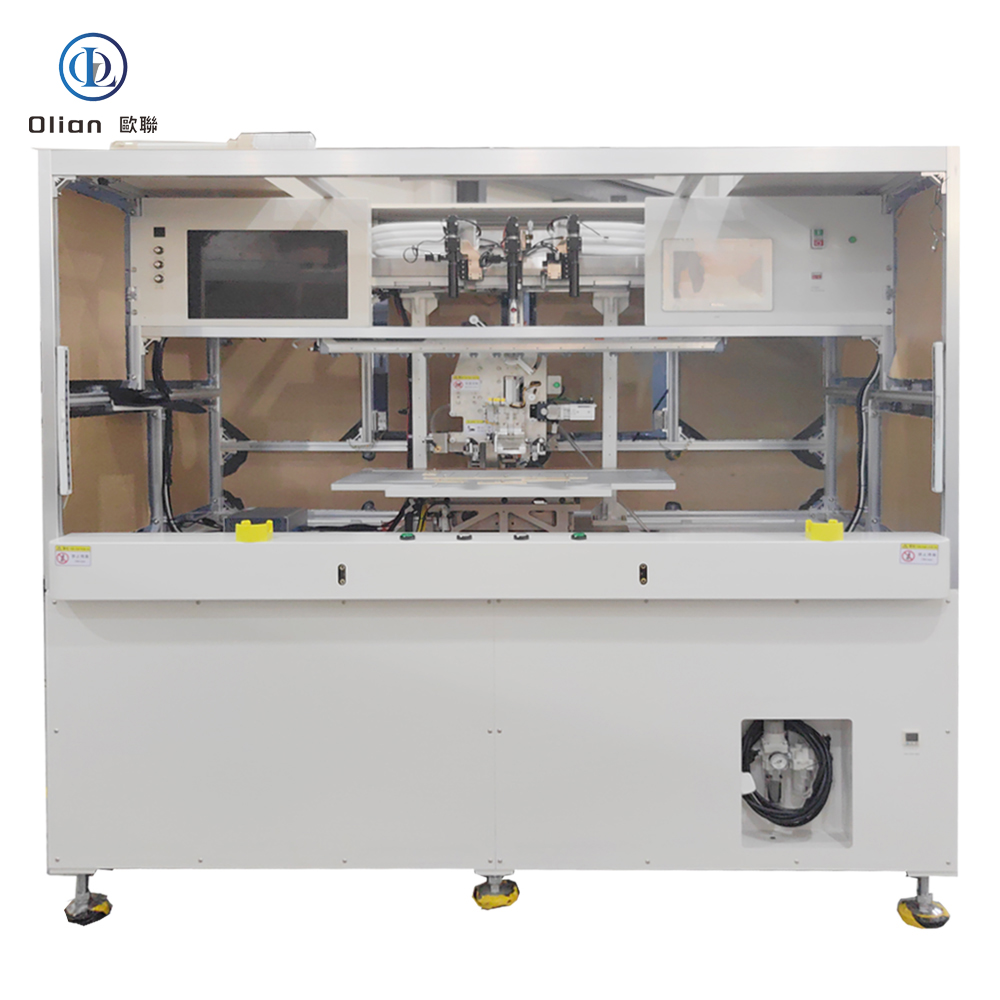
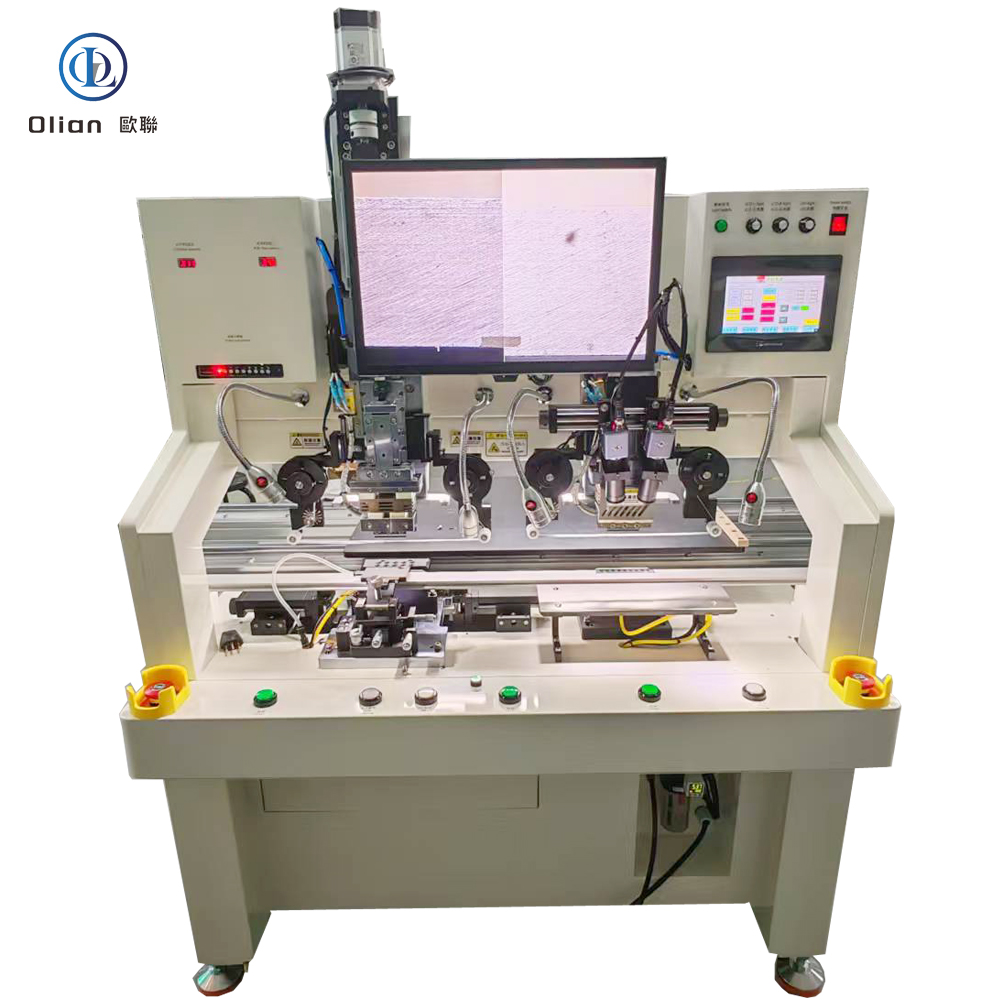
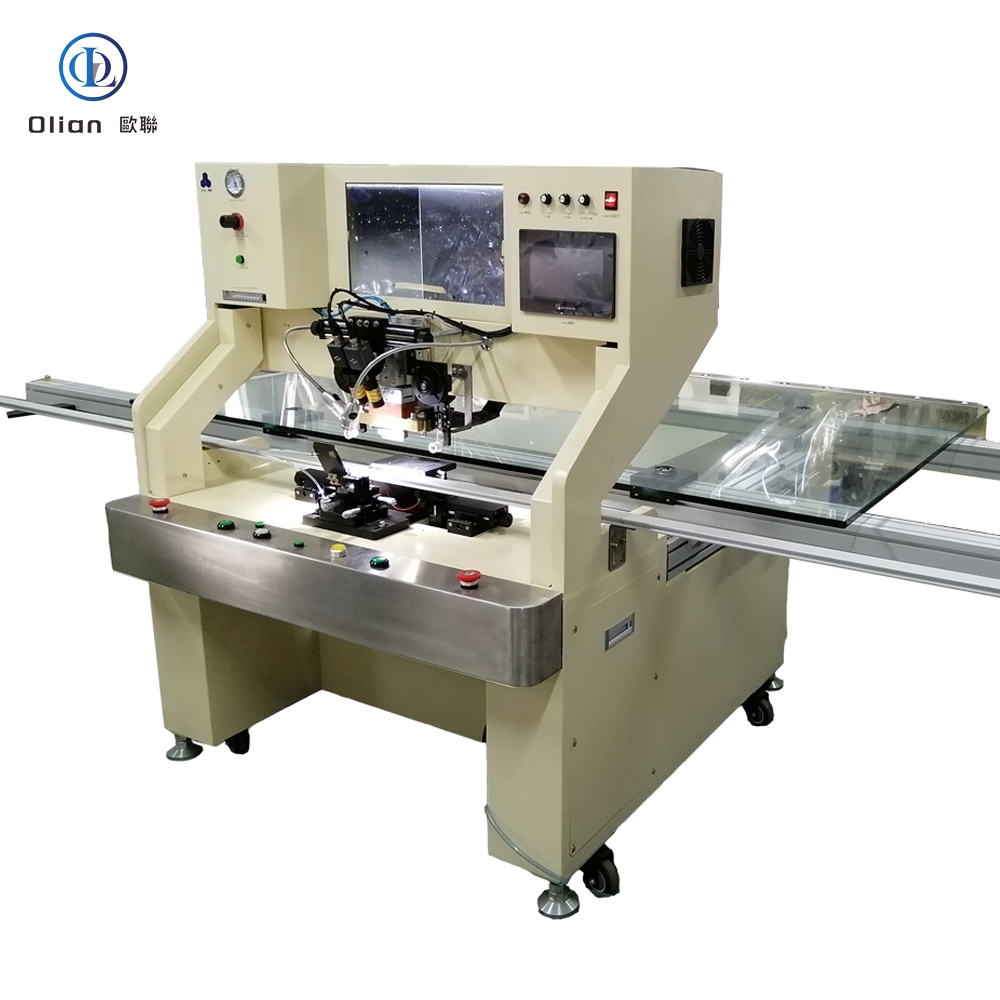
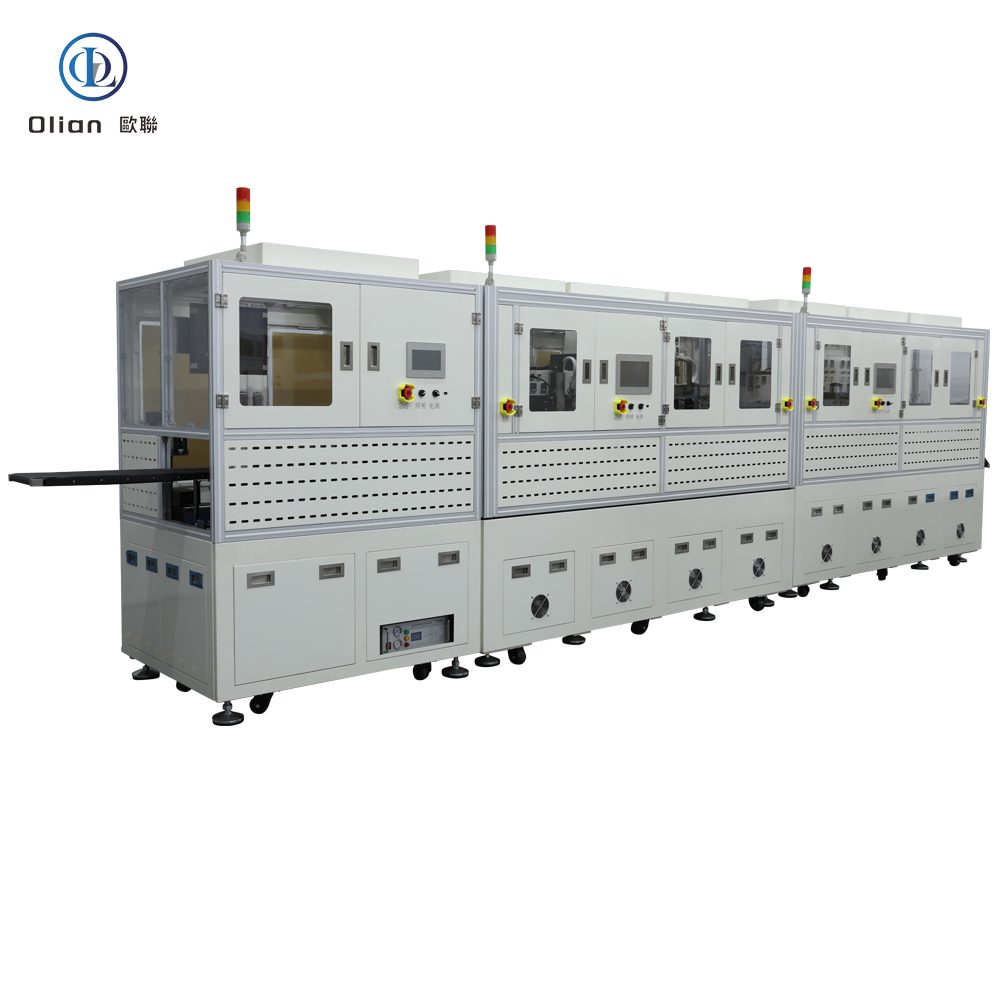
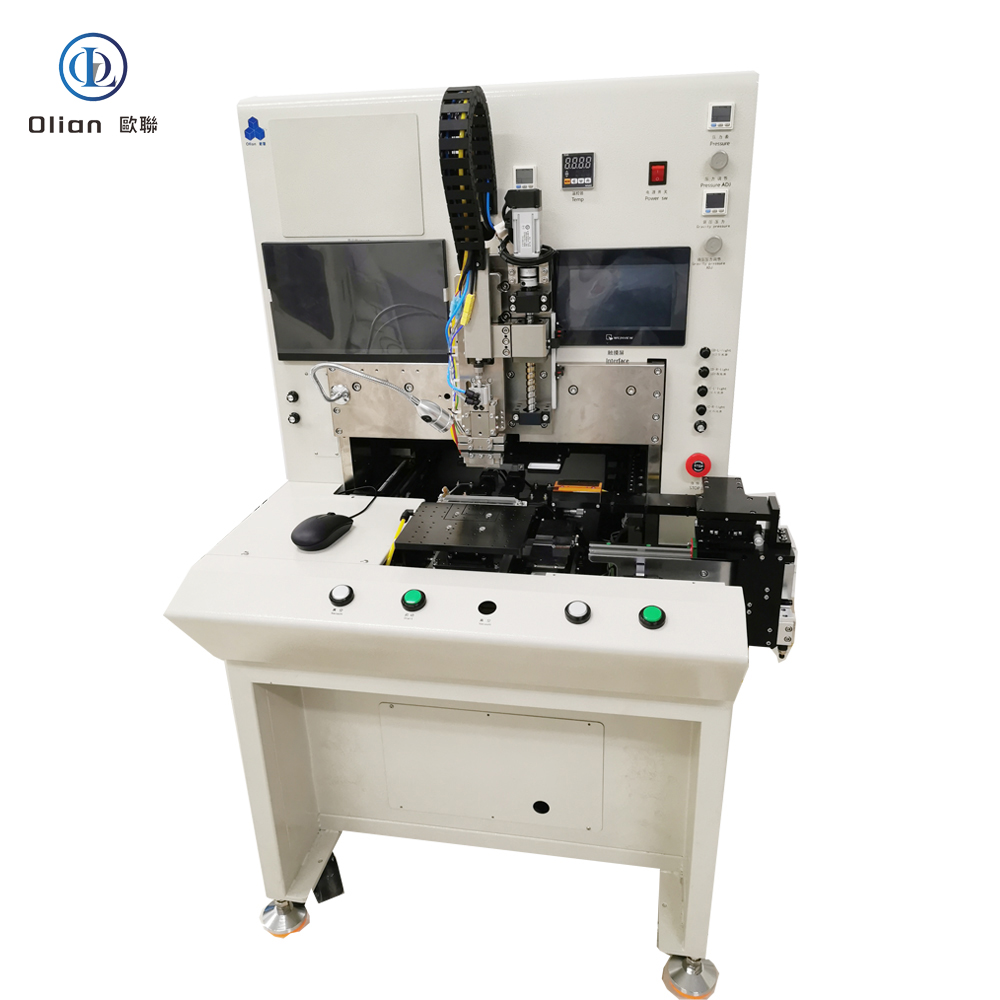
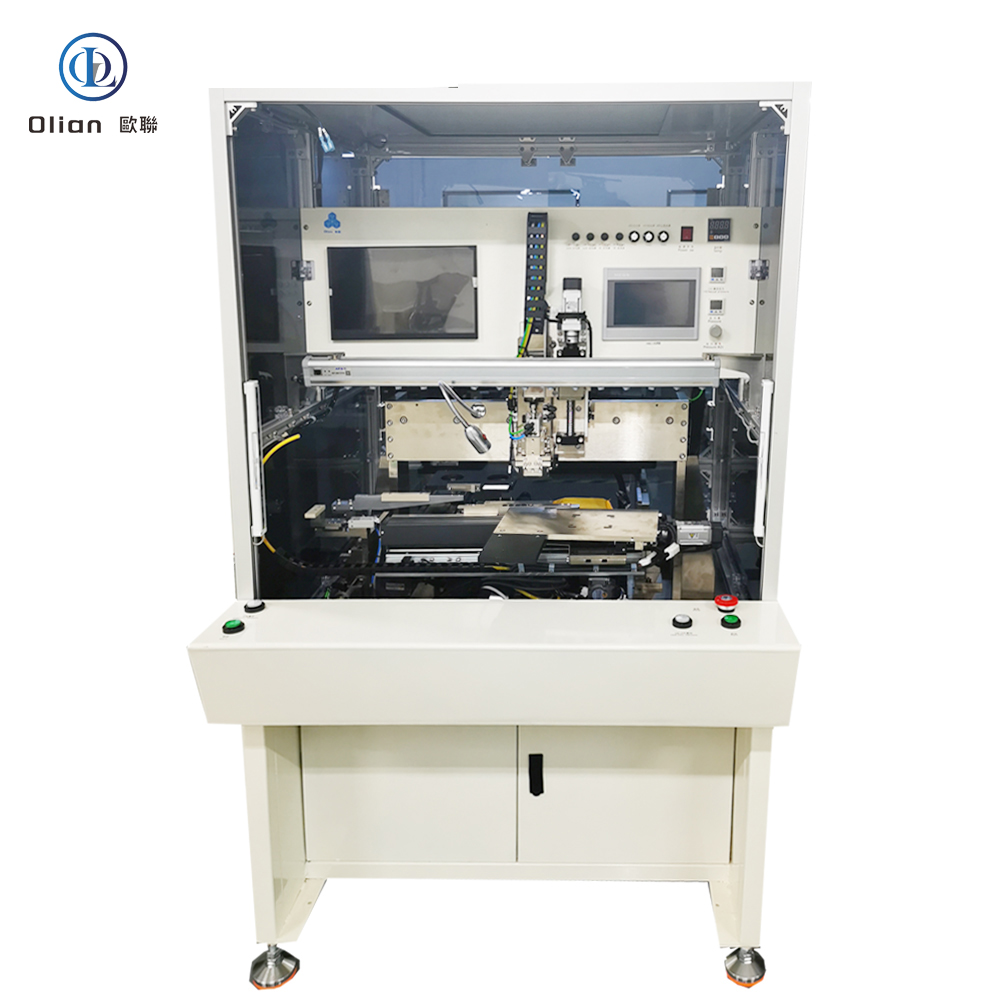
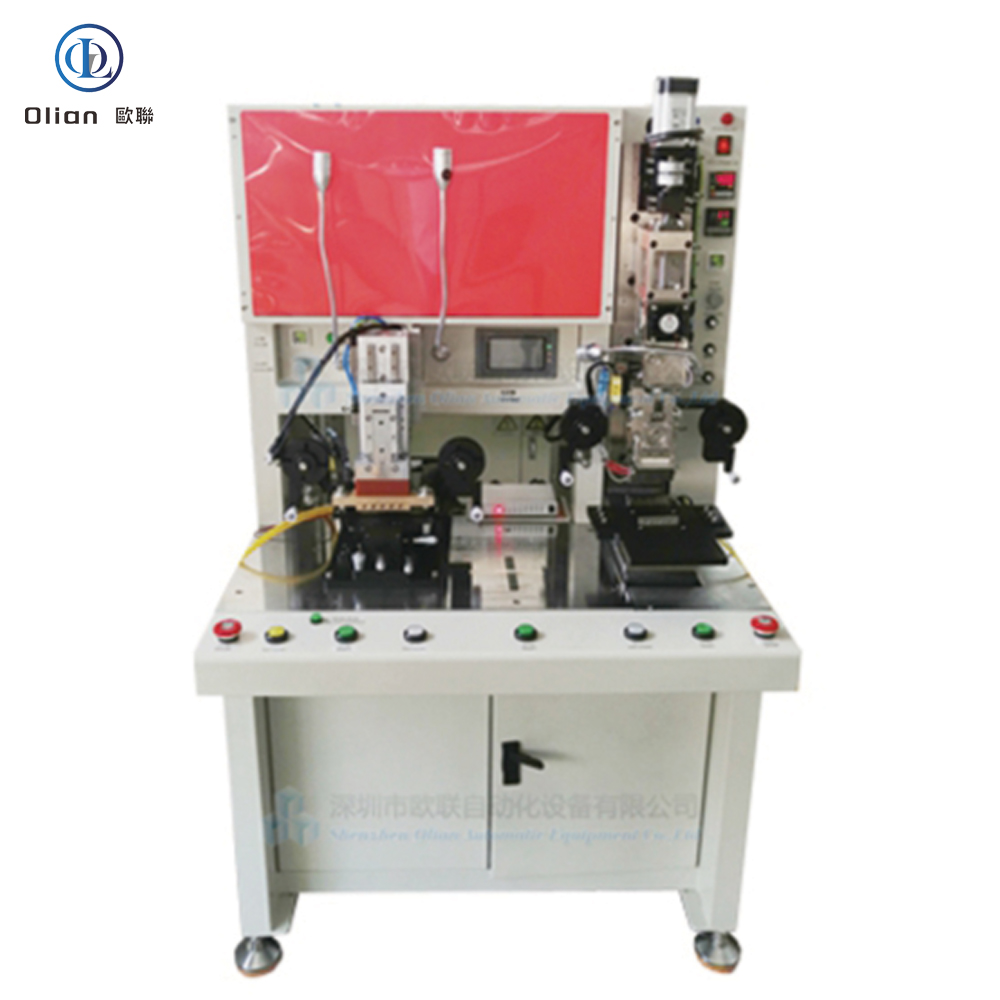
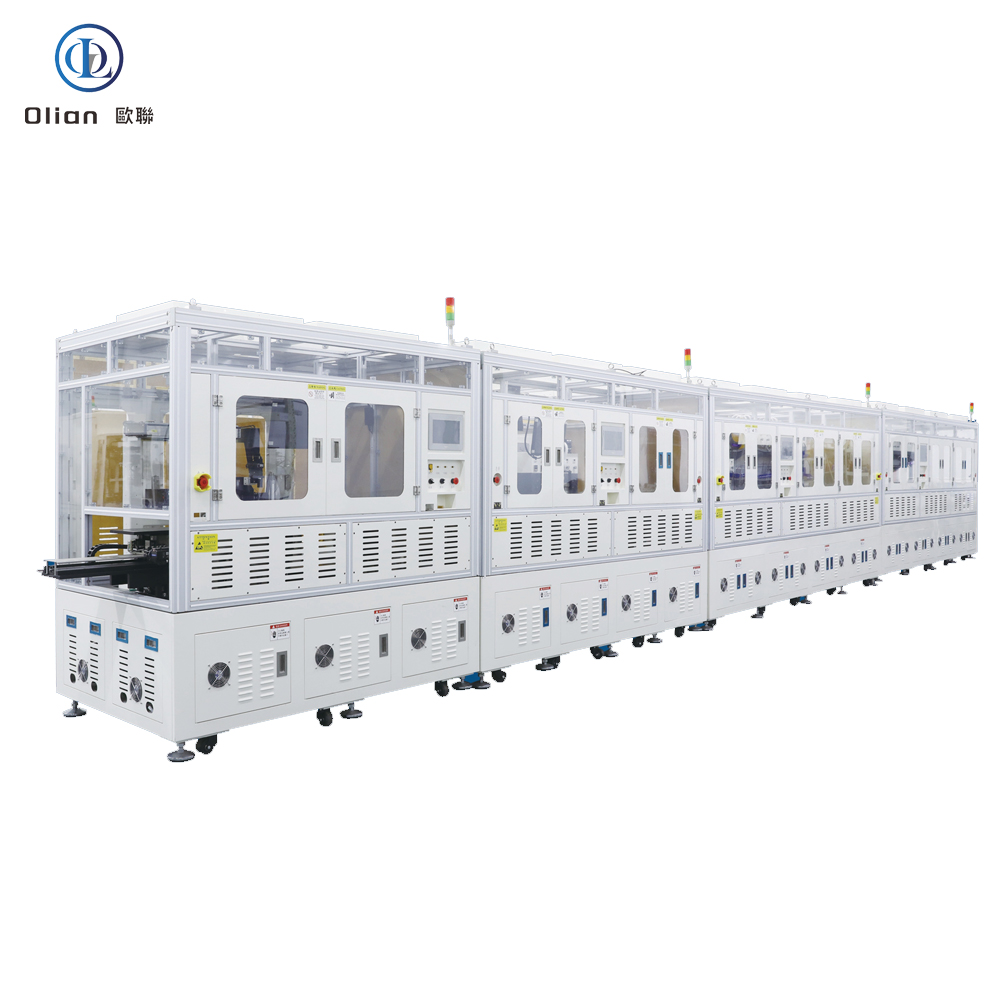
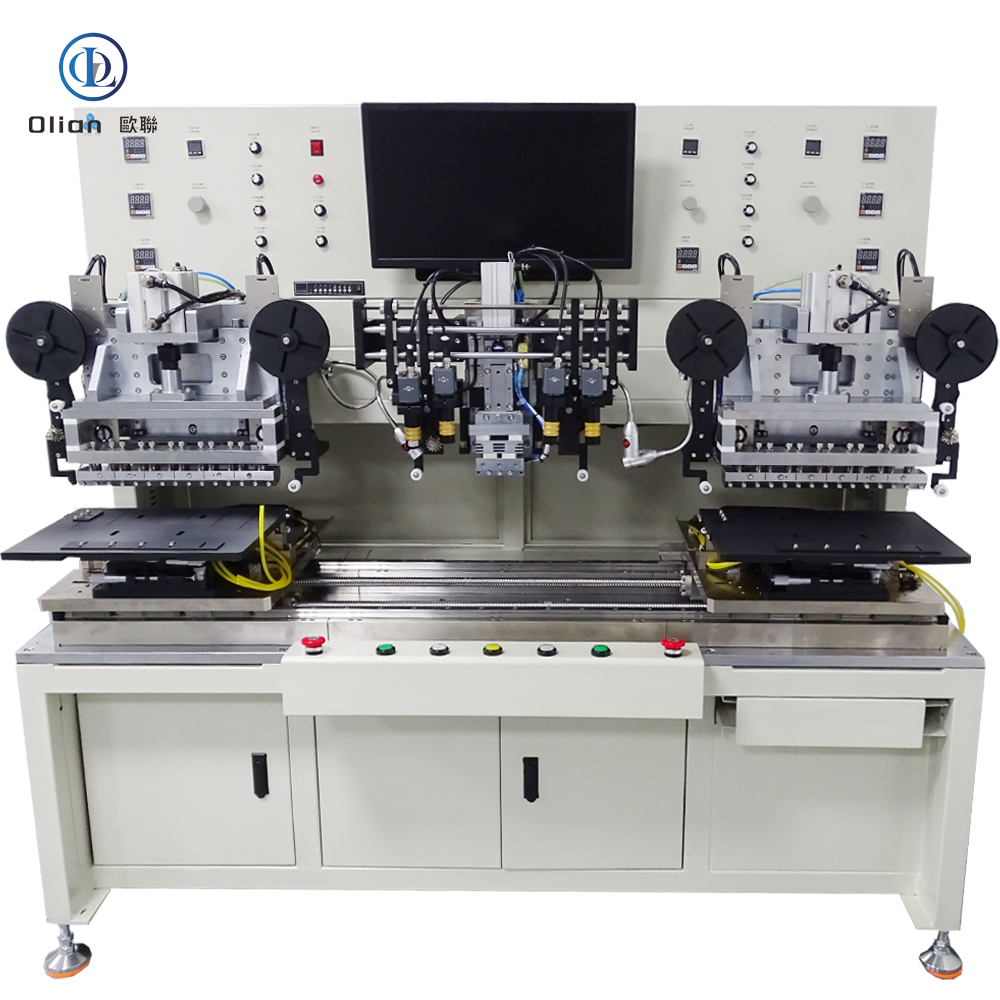










Consumer Electronics: Smartphone OLED, tablet LCD, laptop mini-LED, smartwatch flexible AMOLED.
TV Manufacturing: 32″–100″ 4K/8K panels, 120 Hz and 144 Hz gaming monitors, curved screens.
Automotive: Instrument clusters, center-stack touch displays, head-up projection films.
Medical: High-resolution diagnostic monitors, surgical displays that require narrow bezels for sterile integration.
Industrial: Human-machine interfaces, outdoor kiosks, aviation seat-back entertainment.
This article naturally embeds high-value phrases: COF bonding machine, Chip on Film bonder, ACF bonding equipment, pulse heat bonding, LCD repair COF, TV panel bonding machine, 4K 8K display bonding, flexible film IC bonding, micro-bump bonding, narrow bezel technology, OLED COF bonding, foldable display bonding, laser COF repair, bonding accuracy 1 micron, freezing separator alternative, lead-free bonding, ROHS compliant bonding, China COF bonding machine, automatic COF bonder, COF vs COG comparison.
AI-Driven Alignment: Deep-learning vision predicts thermal drift and pre-corrects position, pushing accuracy below 0.5 µm.
IoT Monitoring: Each head uploads temperature, pressure, and resistance curves to the cloud; machine-learning spots early heater failure and schedules maintenance before scrap occurs.
Green ACF: New conductive particles use copper-silver alloy instead of pure gold, cutting material cost 40%.
Roll-to-Roll Bonding: Reel-fed film and waffle-pack ICs enable continuous bonding for micro-LED transfer, reaching 2000 units/h.
Cold Laser Assist: Femtosecond laser pre-treats the polyimide surface, lowering required bonding temperature to 120 °C, ideal for heat-sensitive flexible OLED.
Servo-Hydraulic Hybrid: Combines speed of servo presses with force stability of hydraulics for 100″ TV COF where 80 kg force is needed.
A COF bonding machine is the critical enabler for ultra-narrow bezels, high refresh rates, and foldable designs. By mastering micron alignment, pulse-heat control, and real-time force feedback, manufacturers can bond driver ICs on flexible film at speeds exceeding one chip every four seconds while maintaining reliability across −40 °C to +85 °C. Whether you run a high-volume TV line or a boutique phone refurbishing shop, investing in the latest AI-enhanced, IoT-connected COF bonding platform future-proofs your process for 8K, micro-LED, and beyond.

An LCD repair machine is a precision system that fixes cracked glass, failed TAB bonds, open ITO lines, color lines, and backlight problems in televisions, laptops, tablets, smartphones, and industrial monitors. Instead of throwing expensive panels away, service centers use these machines to restore original performance at component level. The following long-form article explains every angle of the technology so Google can easily index the keywords “LCD repair machine”, “TV panel repair equipment”, “laser LCD repair”, “TAB bonding machine”, “COF bonding machine”, “LCD freezing separator”, and related phrases.
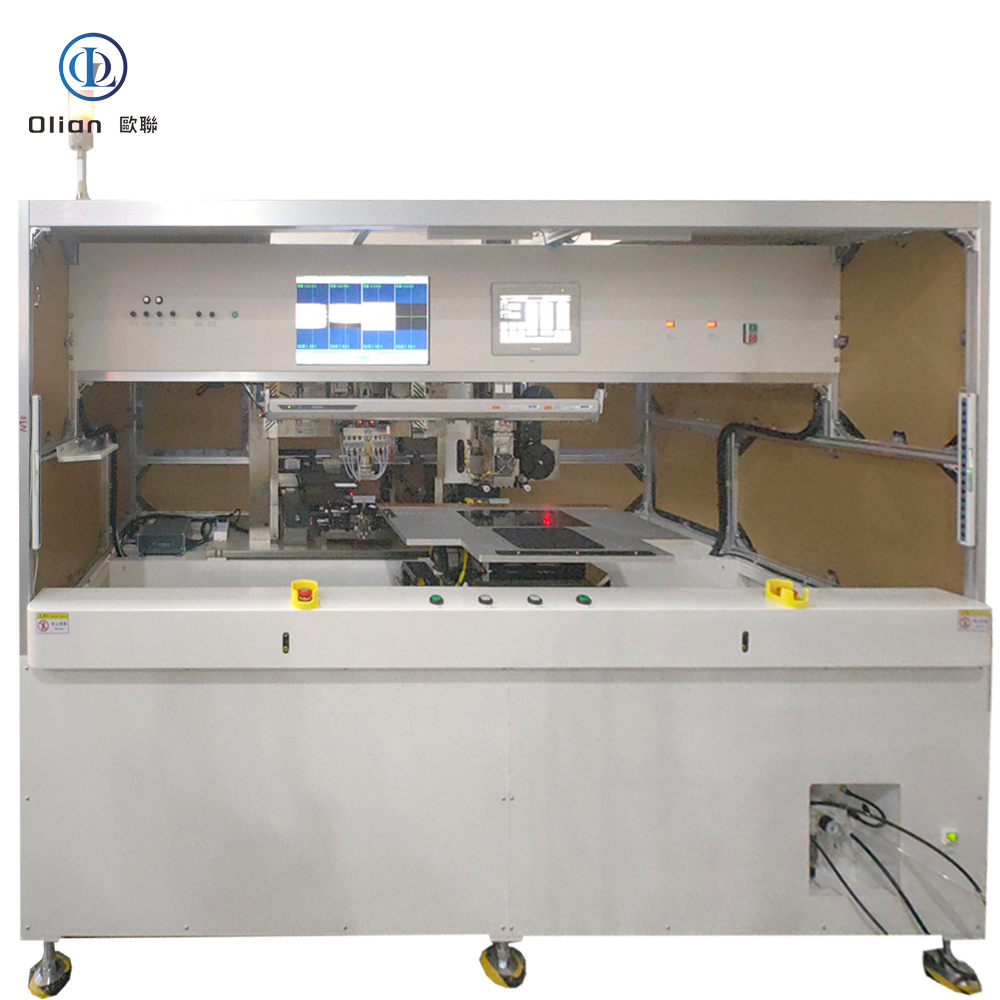
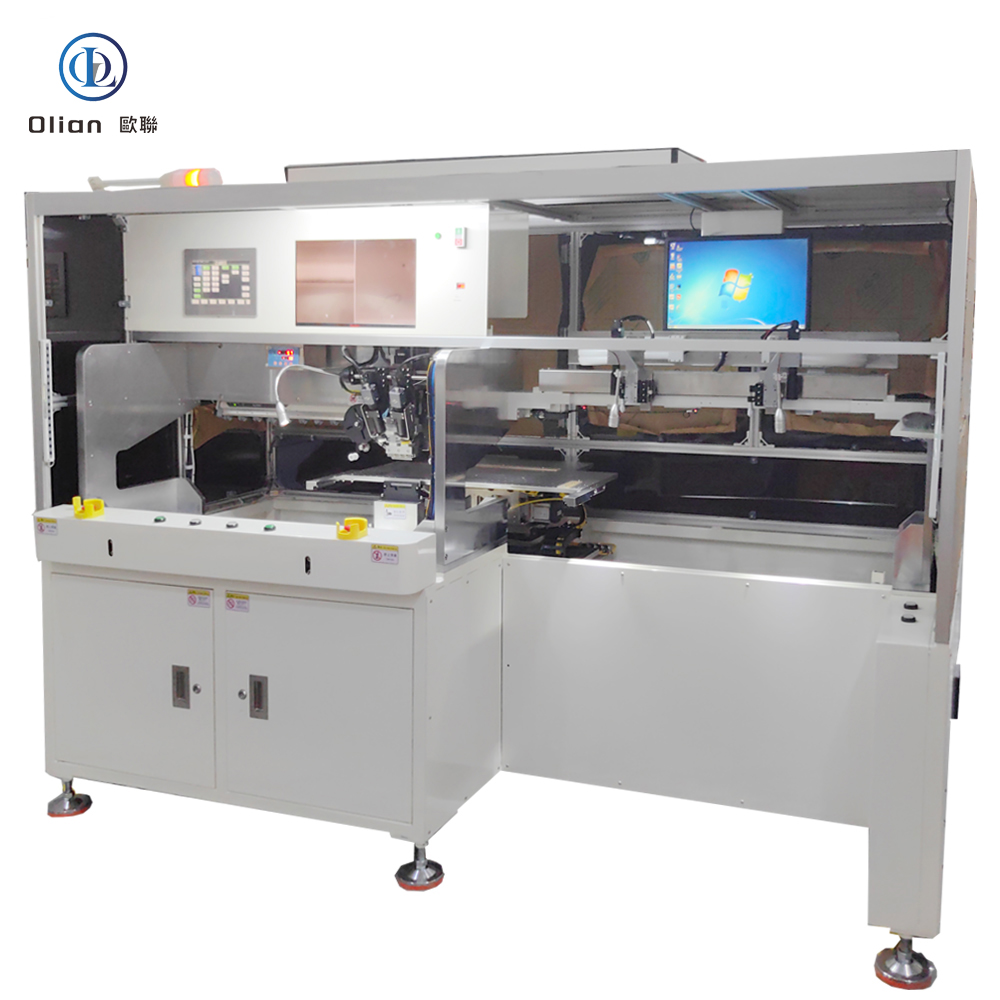
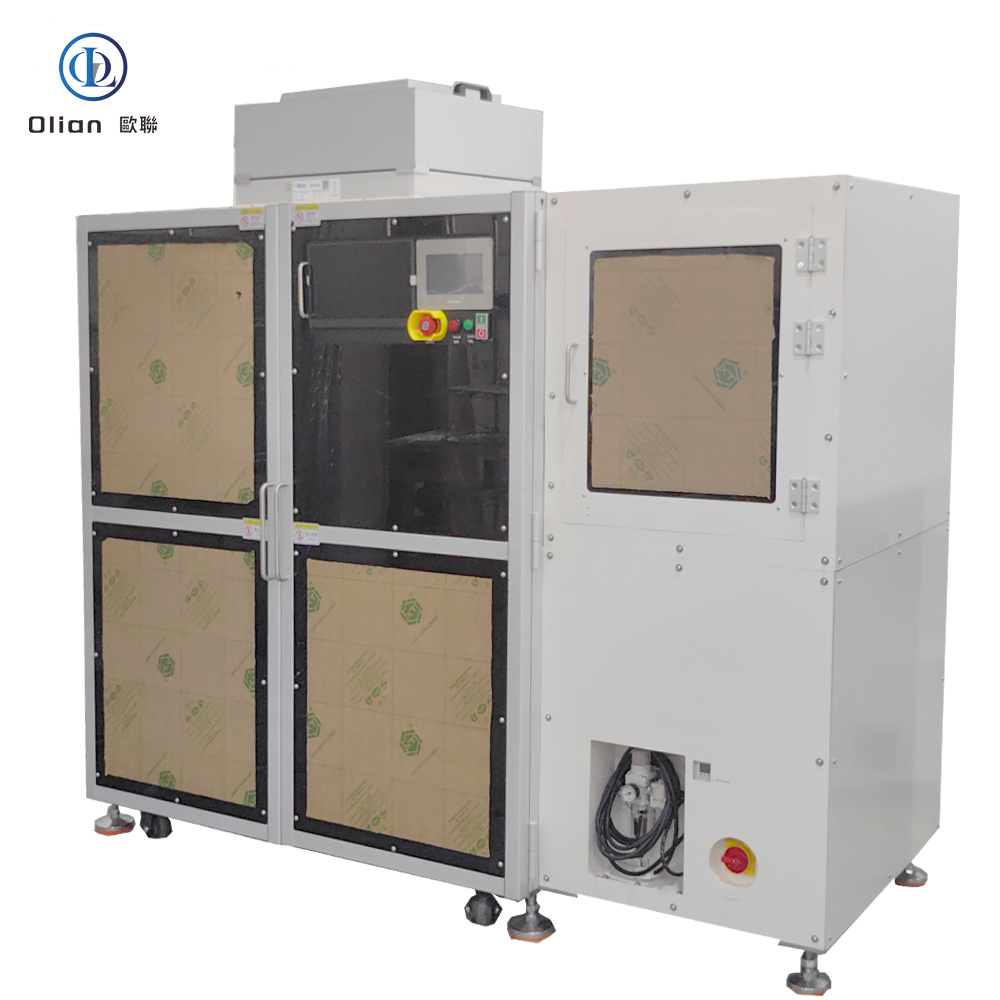
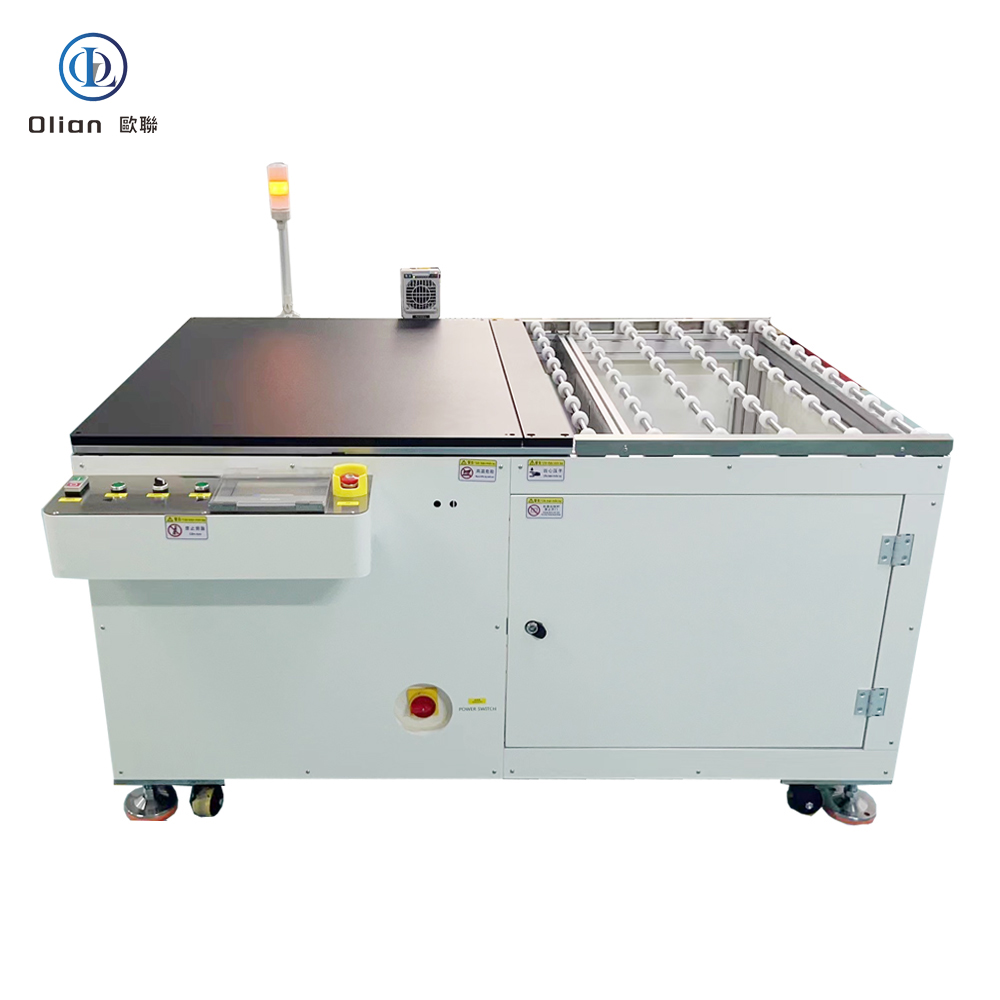
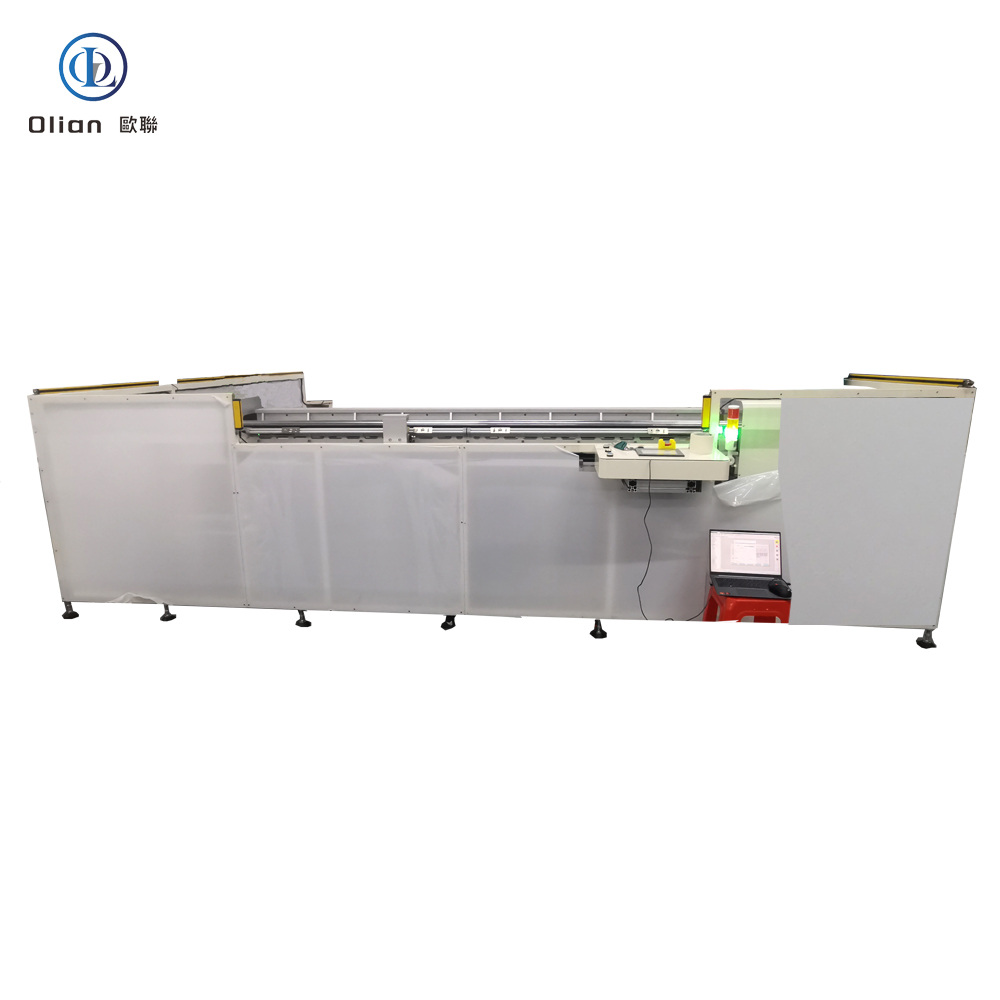
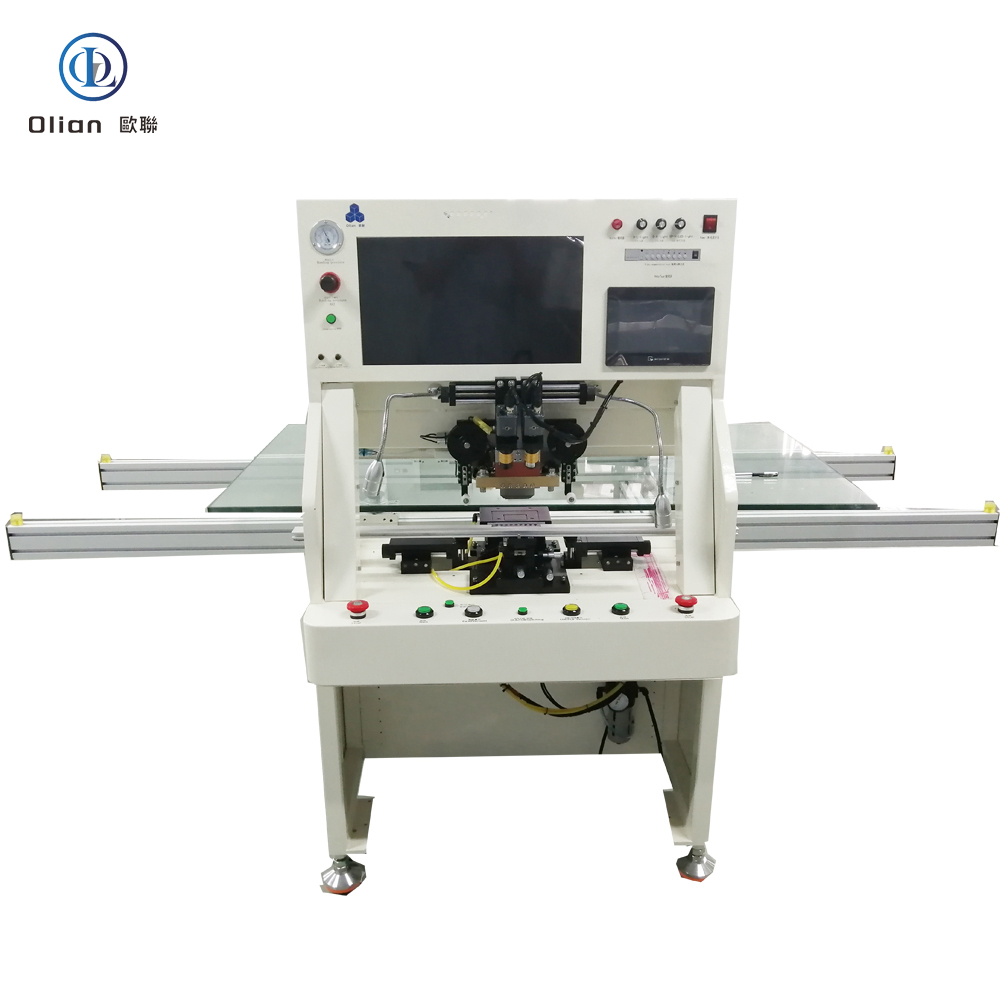
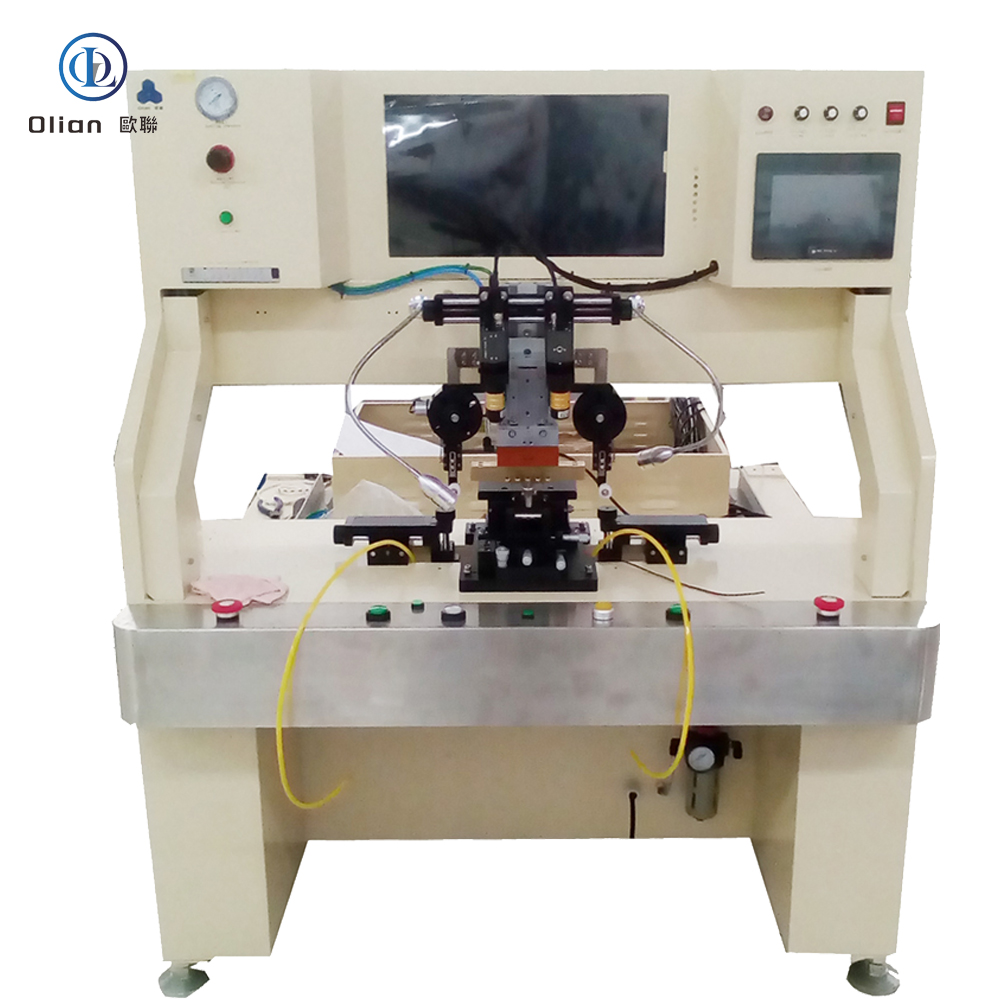
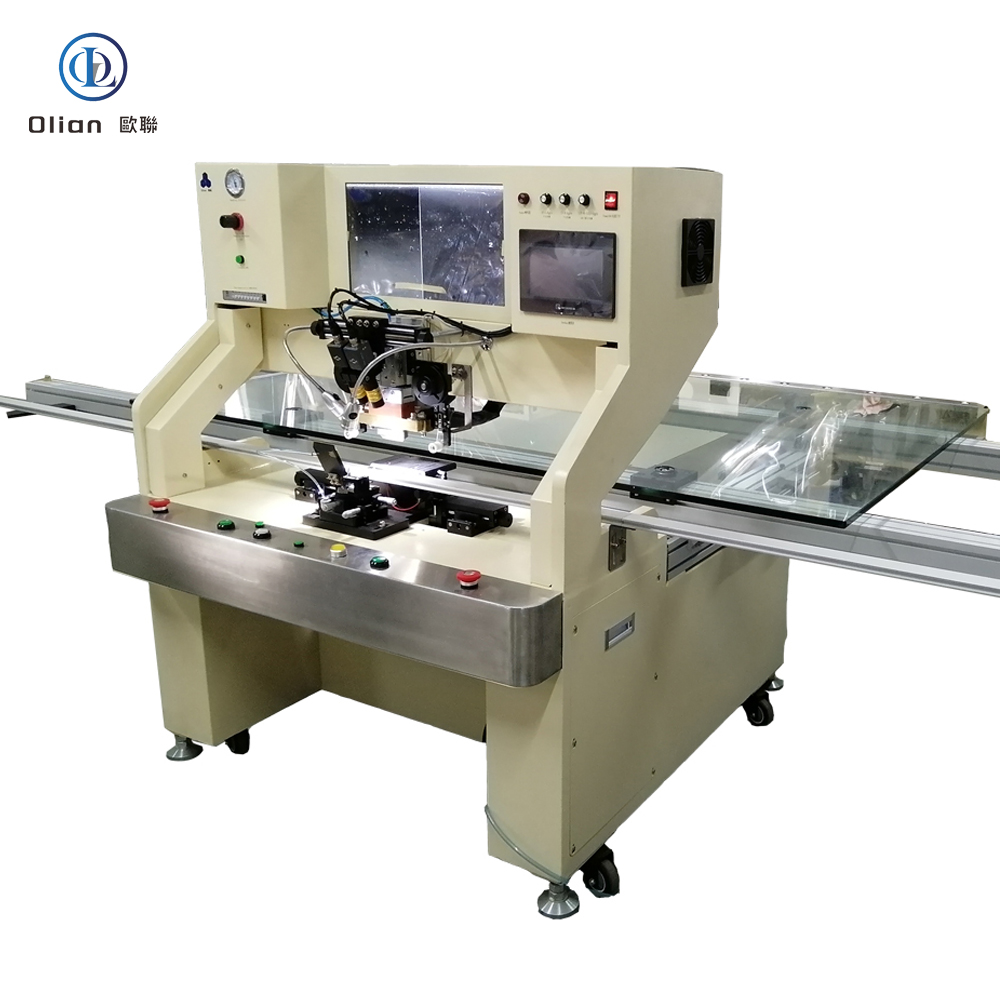
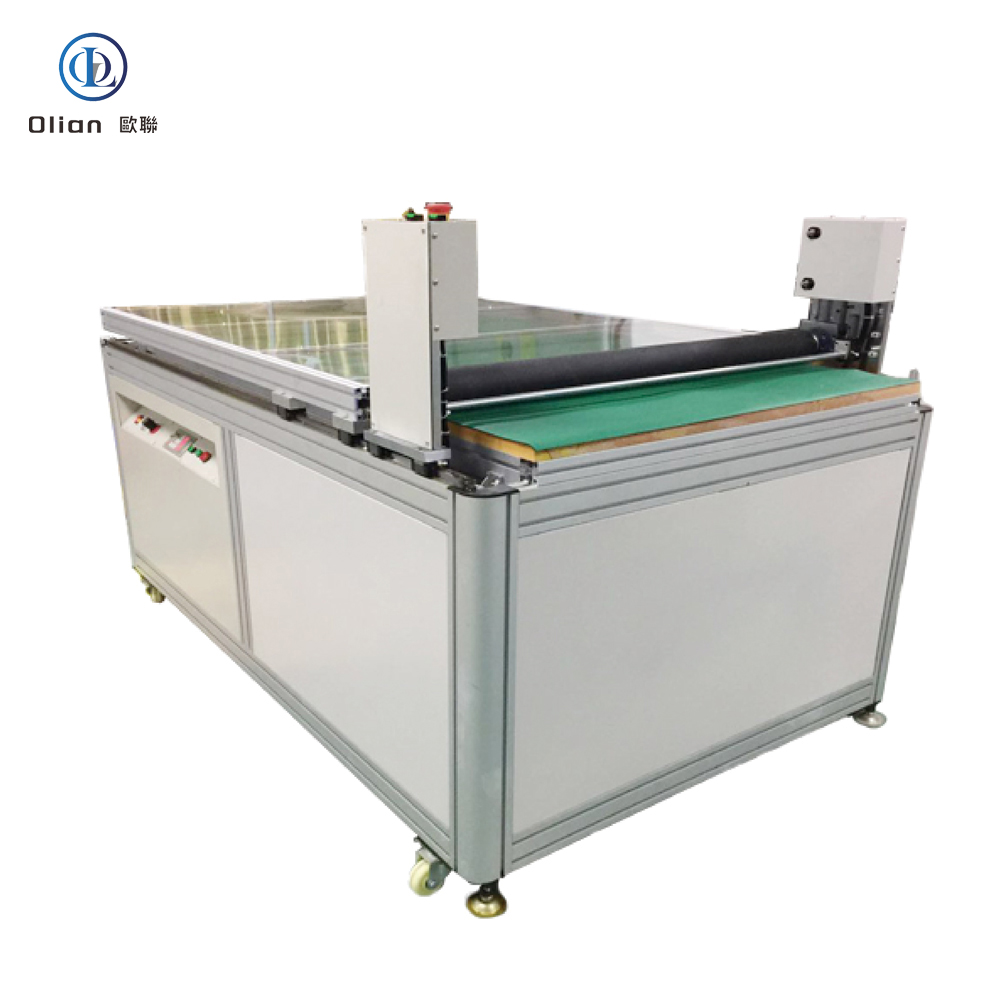
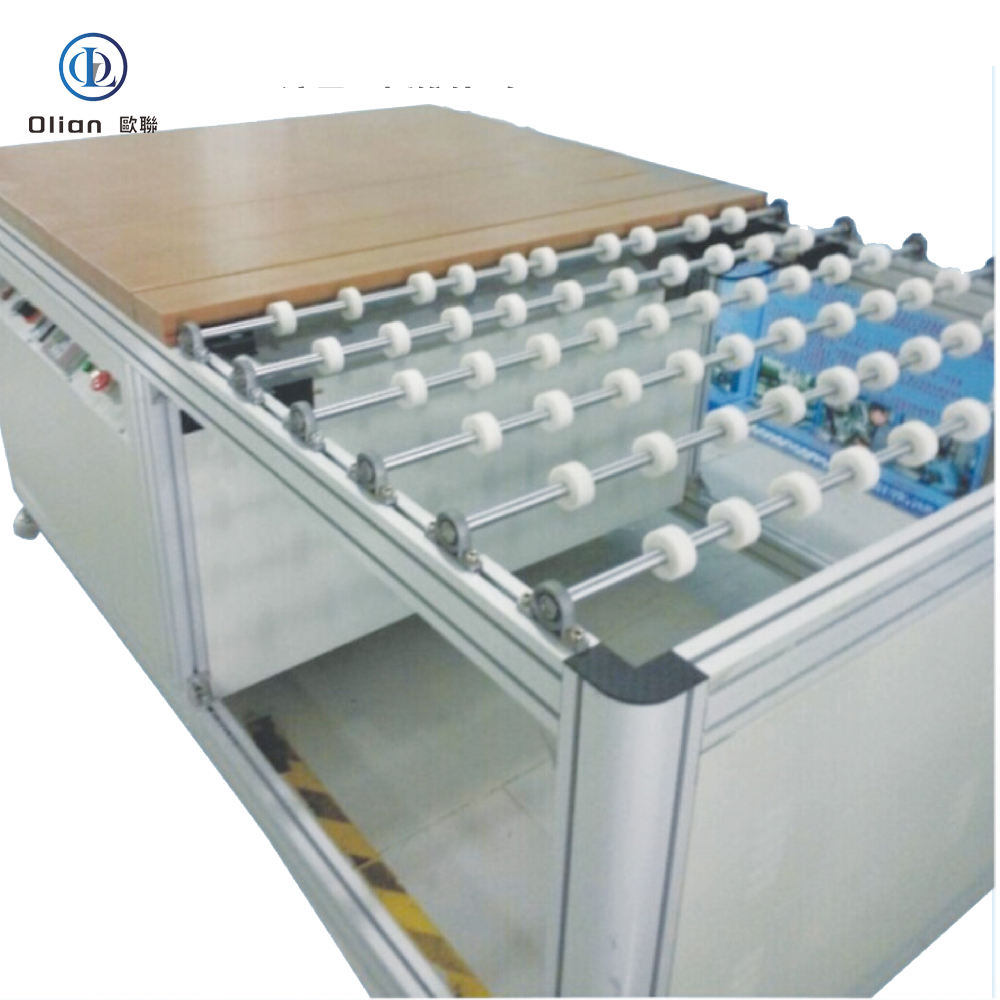
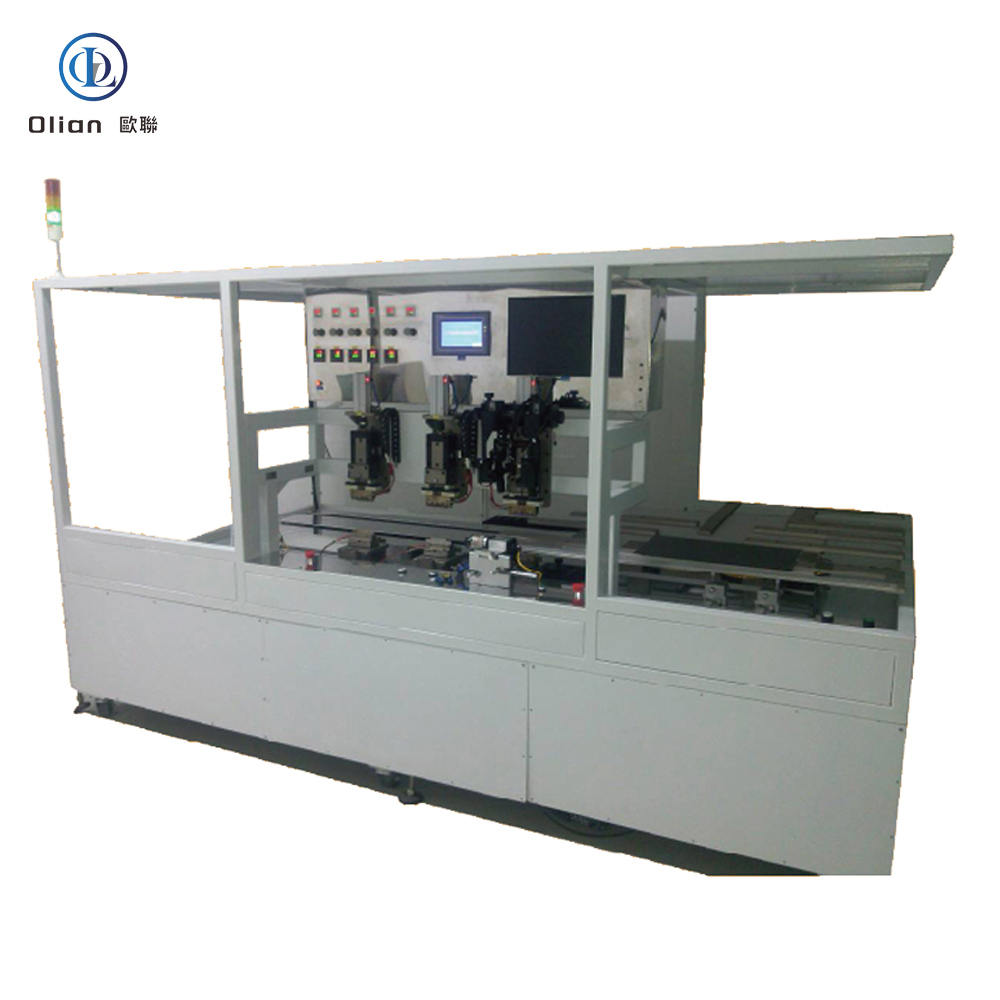
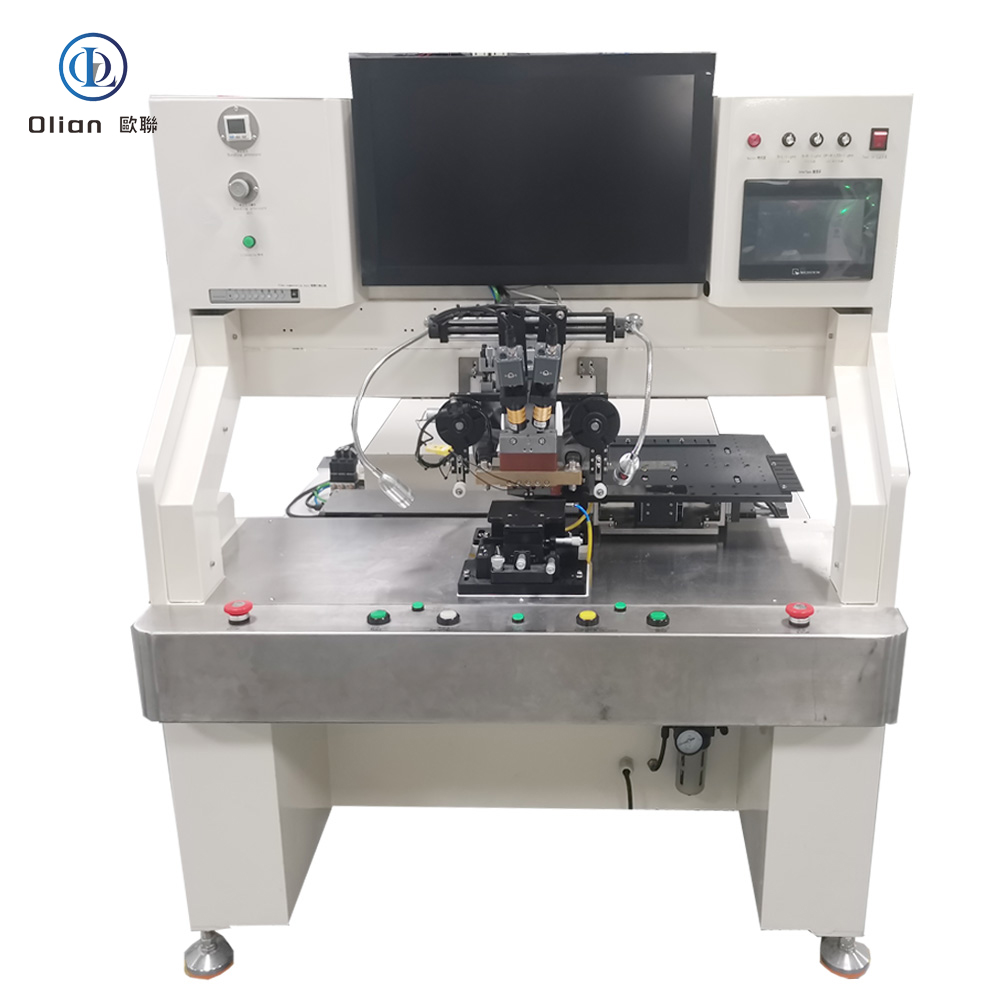
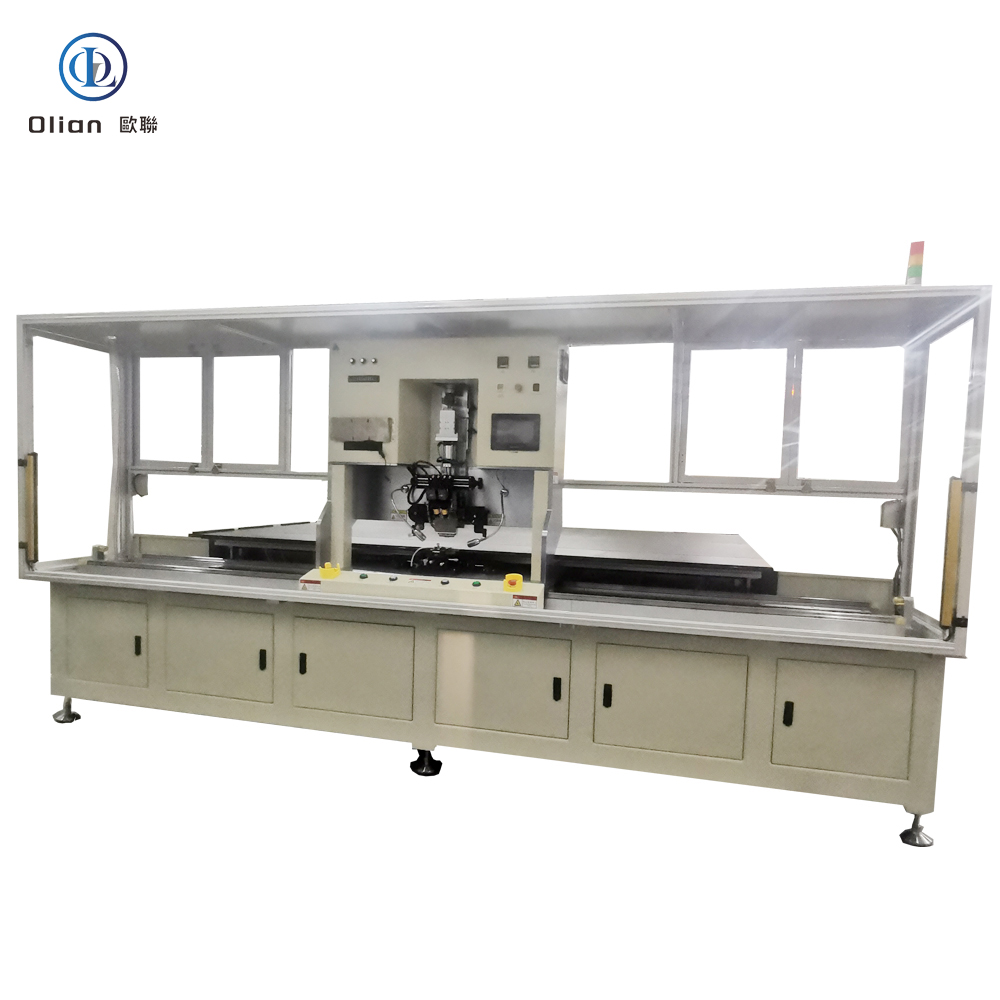

















An LCD repair machine is a collective name for several modules that separate, clean, bond, test, and sometimes laser-trim LCD glass. Each module targets a specific fault: outer glass cracks, polarizer scratches, flex cable delamination, driver IC failure, or internal short/open circuits inside the glass. Professional workshops combine these modules into one production line to handle 5″, 10″, 32″, 55″, 65″, 75″, even 100″ panels with the same daily throughput. The process is lead-free, ROHS friendly, and generates far less e-waste than replacing the whole display.
The freezing separator repairs outer glass damage on phones and tablets. It cools the assembly to minus 140 °C with liquid nitrogen or compressed refrigerant. The low temperature embrittles the OCA glue so a steel wire slides between cover glass and the sensitive OLED or LCD underneath without force. After separation, the machine warms to room temperature, allowing easy pick-up of broken glass and leftover glue removal. The same cabinet can process 30–50 screens per hour with almost zero breakage when operators follow the correct recipe
.
A lower-cost alternative for shops that do not want liquid nitrogen. The hot plate heats the screen to 80–90 °C, while a vacuum chuck keeps the glass flat. A thin cutting wire then separates the glass. The method is slower but adequate for entry-level phone repair businesses.
TAB (tape-automated bonding) and COF (chip-on-film) bonding machines repair flex cable failures in TV panels. A pulse-heated titanium head presses the flex against the LCD pad through anisotropic conductive film (ACF). The head ramps to 180–220 °C in two seconds, holds ±0.3 °C accuracy, then cools quickly to solidify the adhesive while conductive particles create vertical conductivity only. Modern models bond 4K/8K panels up to 100 inches with 1.5 µm alignment accuracy
.
Laser systems fix internal glass defects such as bright lines, dark lines, half-lines, dot defects, short circuits, or ITO opens. A Nd:YAG or fiber laser fires microsecond pulses through a microscope objective to cut or link redundant bus lines inside the panel. Dual-wavelength machines (1064 nm + 532 nm) handle both metal and transparent oxide layers. Spot size can be as small as 3 µm, so the repair is invisible to the naked eye
.
After glass replacement or laser trimming, a new polarizing film must be laminated without dust or bubbles. The laminator uses a rubber roller in a Class-100 clean chamber to apply even pressure. A subsequent autoclave heats the stack to 45 °C under 0.4 MPa for 20 minutes to eliminate micro-bubbles.
LCD repair machine, TV panel repair equipment, laser LCD repair, TAB bonding machine, COF bonding machine, ACF bonding equipment, LCD freezing separator, polarizer laminator, LCD refurbishing machine, smartphone screen repair tools, 4K panel bonding, 100 inch LCD repair, internal line repair laser, ITO open repair, vertical line fix, horizontal line fix, dot defect removal, pulse heat bonding, fine-pitch bonding, lead-free LCD repair, ROHS compliant repair, e-waste reduction, sustainable display repair.
AI-driven vision will auto-select laser cut or link paths, reducing technician training time. IoT modules will send yield data to cloud dashboards for predictive maintenance. Green refrigerants will replace liquid nitrogen in freezing separators, cutting operating cost by 30%. Roll-to-roll ACF will enable continuous bonding of ultra-wide 110″ panels. Micro-LED hybrid displays will adopt the same laser micro-machining platforms, extending the machine’s useful life well into the next decade.
An LCD repair machine is no longer a single-purpose tool; it is a strategic investment that restores value to damaged displays, supports environmental goals, and delivers rapid return on investment across smartphones, TVs, laptops, automotive, and industrial applications. By choosing the right combination of freezing separation, TAB/COF bonding, laser trimming, and polarizer lamination modules, service centers can handle virtually any LCD faults. Shenzhen Olian to be the LCD repair machine’s one stop supplier..

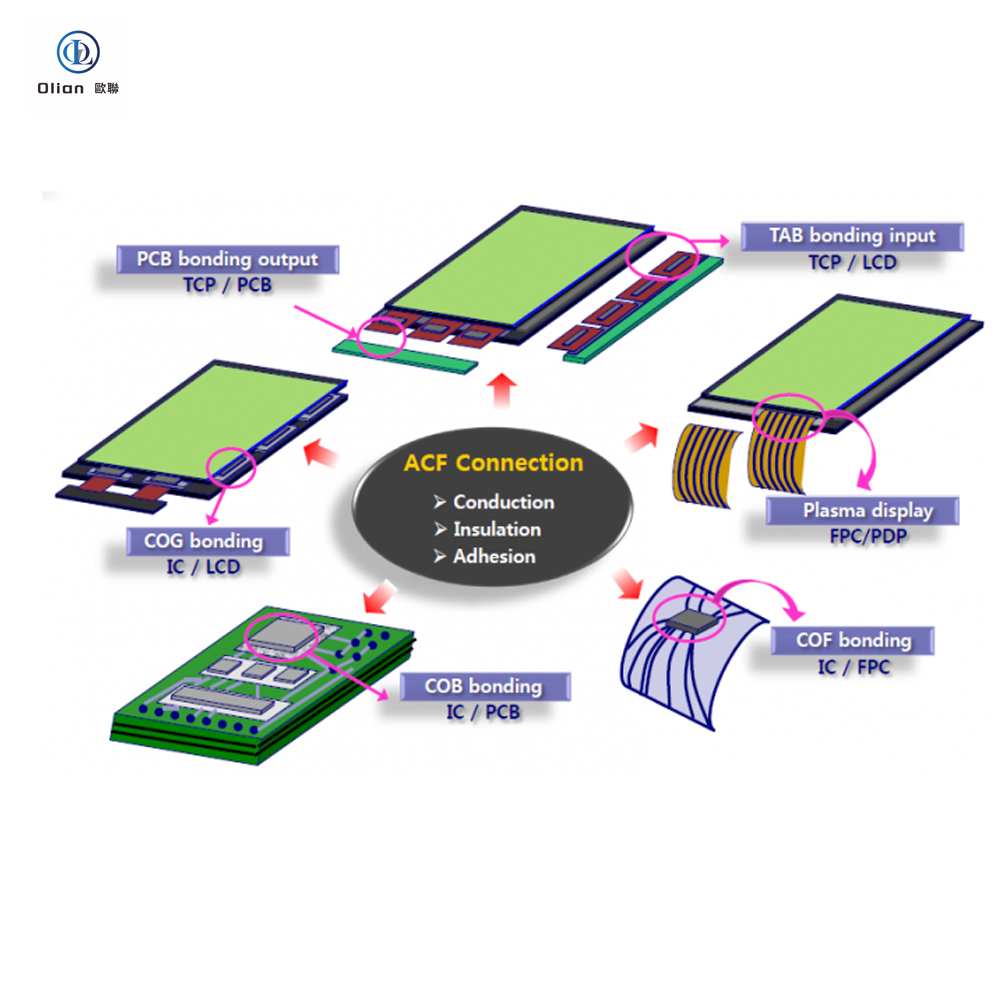
ACF bonding machine
What is an ACF bonding machine?
ACF stands for Anisotropic Conductive Film. ACF bonding machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to create reliable electrical connections between flexible and rigid electronic components. This article will provide a detailed overview of ACF bonding machines, covering their definition, working principles, applications, advantages, and more.
An ACF bonding machine is a device that utilizes Anisotropic Conductive Film to bond electronic components, such as flexible printed circuits (FPCs), flexible flat cables (FFCs), and integrated circuits (ICs), to substrates like glass or printed circuit boards (PCBs). The machine applies precise heat, pressure, and time parameters to ensure a secure and conductive connection. The primary function of the ACF bonding machine is to enable electrical conductivity in the vertical (Z-axis) direction while maintaining insulation in the horizontal (X and Y-axis) directions, thus preventing short circuits between adjacent circuits.
The working principle of an ACF bonding machine involves several key steps:
ACF bonding machines are widely used in various industries, including:
The use of ACF bonding machines offers several advantages:
Modern ACF bonding machines come with a range of technical specifications to meet diverse manufacturing needs:
Proper maintenance and safety protocols are essential for the optimal operation of ACF bonding machines:
ACF bonding machines are indispensable in the electronics manufacturing industry, providing a reliable, efficient, and cost-effective solution for creating high-quality electrical connections. Their ability to bond fine-pitch components with precision and flexibility makes them ideal for a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices. As technology continues to advance, ACF bonding machines will remain a critical tool in the production of next-generation electronic devices.
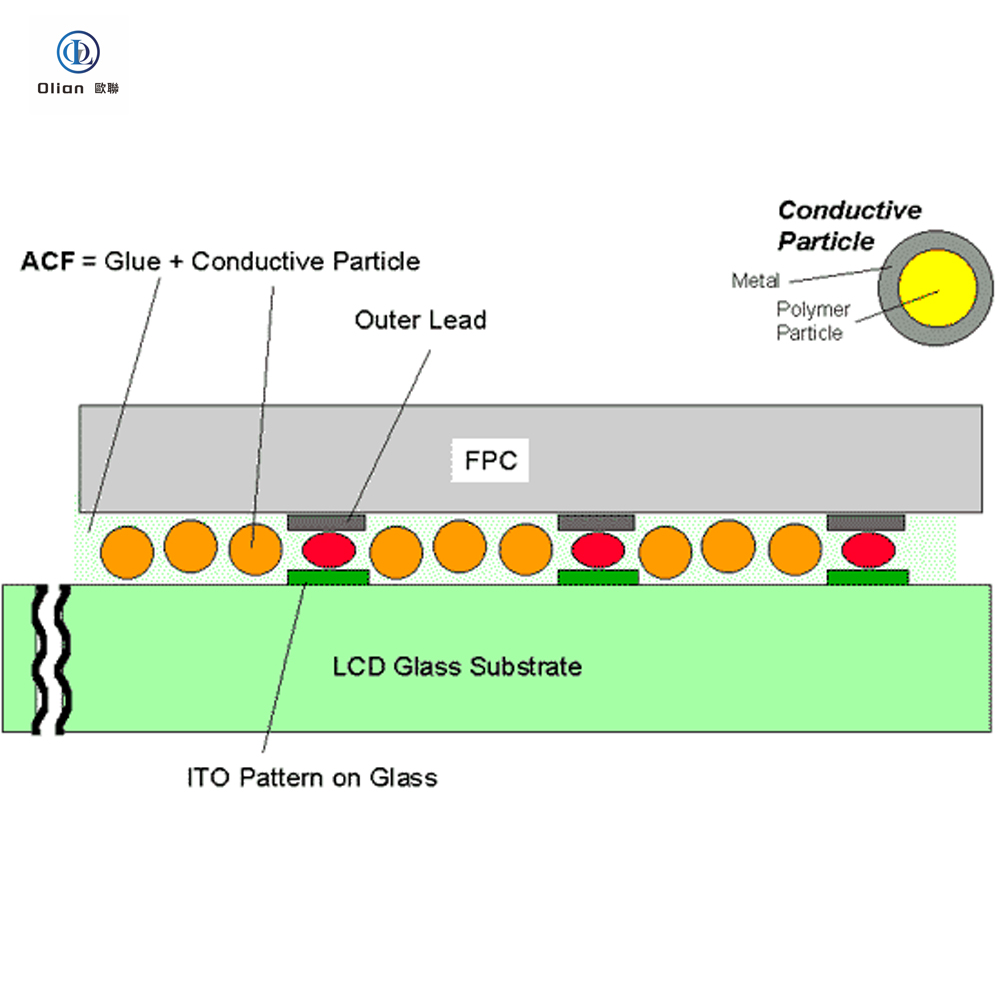
ACF bonding uses anisotropic conductive film.
It creates vertical conductivity and horizontal insulation.
The film holds tiny conductive particles in adhesive.
Heat and pressure activate the particles.
Only the Z-axis becomes conductive.
This prevents short circuits between adjacent traces.
ACF bonding is clean and lead-free.
It suits fine-pitch flexible assemblies.
A robust frame ensures thermal stability.
Precision heaters raise temperature quickly.
Programmable pressure cylinders apply even force.
High-resolution cameras align parts accurately.
Vacuum chucks hold substrates flat.
Touch-screen HMI sets recipes easily.
Safety shields protect operators from heat.
Data ports log every bond parameter.
First, the operator loads ACF onto substrate.
Vision cameras detect fiducial marks automatically.
The machine aligns flex to glass.
Bond head descends with controlled pressure.
Pulse heat ramps to target temperature.
Adhesive flows and particles touch pads.
Cooling solidifies the joint within seconds.
The head lifts; the circuit is connected.
Smartphone OLED displays rely on ACF bonding.
Tablet touch sensors use the same process.
Vehicle dashboards need durable flex connections.
Medical wearables demand biocompatible joints.
Industrial cameras require vibration-proof bonds.
AR glasses pack ultra-fine pitch traces.
All benefit from ACF’s reliable conductivity.
ACF needs no flux or cleaning.
It tolerates bending and thermal cycling.
Pitch below 30 µm is achievable.
The bond is shock-resistant and lightweight.
Production throughput is higher and greener.
Overall cost per joint drops significantly.
Temperature range: ambient to 500 °C.
Force accuracy: ±0.1 N across range.
Alignment precision: ±3 µm at 3σ.
Cycle time: under 8 seconds per bond.
Heater cooling: forced air or water.
Camera magnification: 2× to 10× selectable.
Machine footprint: 600 mm × 700 mm.
Power supply: single-phase 220 V.
Evaluate your substrate size first.
Check required temperature and force profiles.
Match camera resolution to pad pitch.
Decide between manual and automatic loading.
Request bond-pull data from suppliers.
Ask for local service and spare parts.
Compare software ease and traceability features.
Finally, balance price with throughput needs.
Clean bond head with lint-free wipe.
Inspect heater for adhesive residue daily.
Verify pressure sensor calibration weekly.
Update vision fiducial library after product change.
Keep filters clean on cooling fans.
Log temperature curves for every shift.
Store ACF rolls sealed and refrigerated.
Train operators on safety procedures regularly.
AI vision will self-correct alignment errors.
IoT modules will predict heater failures.
Laser-assisted heating will shorten cycle times.
recyclable ACF will reduce environmental impact.
Nano-silver particles will lower resistance further.
All trends aim for higher yield and speed.

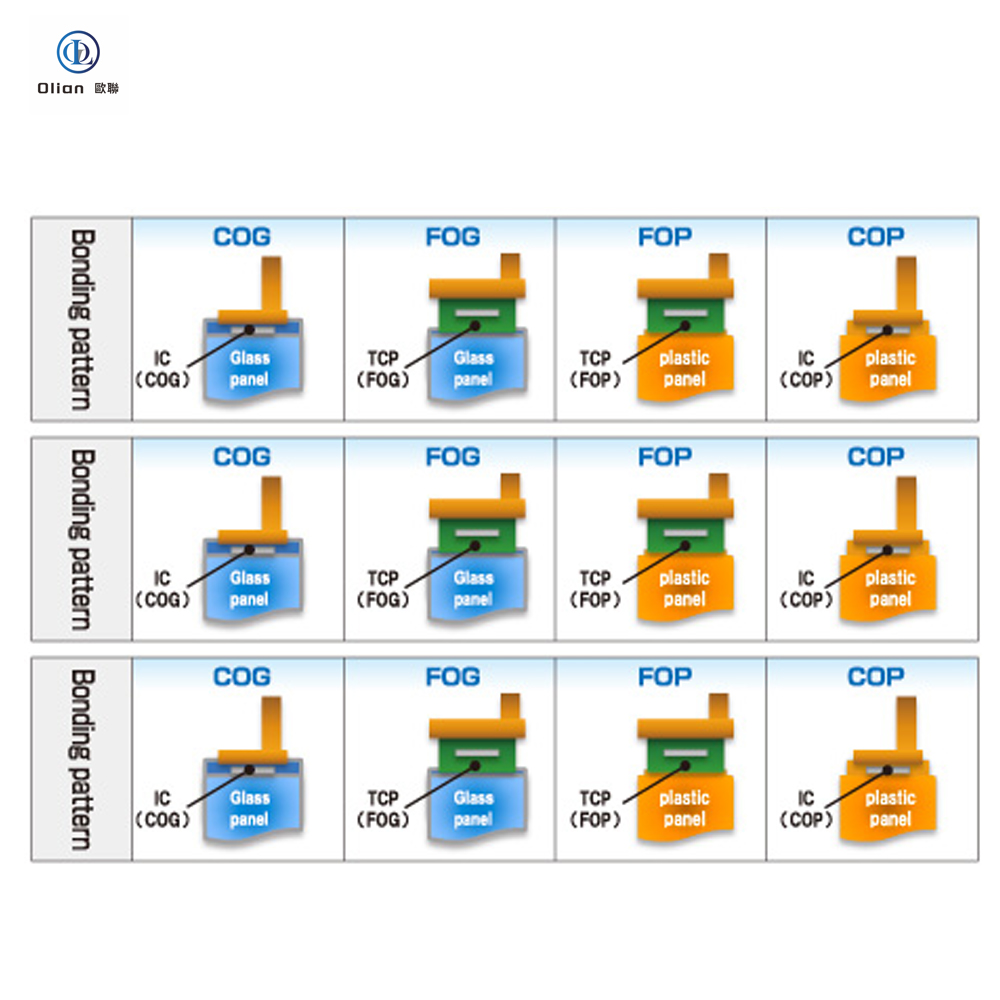
Full Automatic COG/COF/COP Bonding Machines.
Full-automatic COG (Chip On Glass), COF (Chip On Film), and COP (Chip On Plastic) bonding machines are advanced pieces of equipment used in the electronics industry, particularly for the production of liquid crystal displays (LCDs) and other display technologies. These machines automate the process of bonding integrated circuits (ICs) and flexible printed circuits (FPCs) to glass or plastic substrates, ensuring high precision and reliability. Here is a detailed classification and introduction to these machines:
COG bonding machines are used to bond ICs directly onto glass substrates. These machines are crucial for the production of compact and lightweight displays, such as those found in smartphones, tablets, and computer monitors.
COF bonding machines are used to bond ICs onto flexible film substrates. These machines are essential for the production of flexible and lightweight displays, such as those used in foldable devices and wearable technology.
COP bonding machines are used to bond ICs onto plastic substrates. These machines are ideal for applications where flexibility and durability are required, such as in automotive and industrial displays.
Full Automatic COG/COF/COP Bonding Machines are essential in modern electronics manufacturing, providing reliable and efficient solutions for the production of high-quality displays and electronic devices. These machines offer high precision, increased productivity, and reduced labor costs, making them ideal for various applications in consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial sectors. By choosing the right bonding machine, manufacturers can ensure high-quality and efficient production processes, meeting the demands for smaller, more efficient electronic devices.
TFT panel produce processes from bonding to backlight assembly.
TFT LCD Module produce processes .

Automatic FOB Bonder OL-PB3000
Equipment Overview
The OL-PB3000 Automatic FOB Bonder, manufactured by Shenzhen Olian Automatic Equipment Co., Ltd., is a cutting-edge device designed for the automatic PCB loading, ACF (Anisotropic Conductive Film) attachment, alignment, and thermal compression between FOG (Flexible On Glass) products and PCB (Printed Circuit Board) in LCD products ranging from 5.5″ to 17.3″. This equipment is compatible with single-edge multi-segment FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit) products and can be integrated with other machines from the same company to form a production line.
Device Structure and Workflow
The device consists of several key components, including PCB loading, FOG loading, pre-main pressing platform, detection platform, and an outfeeding system. Its workflow starts with PCB loading, followed by FOG loading. Then, the PCB undergoes plasma cleaning. Subsequently, the FOG is transferred to the pre-main pressing platform, and the PCB is also moved to this platform. After alignment between FOG and PCB, the main pressing process takes place. Post pressing, the product undergoes various detection processes. If any deviation is detected, the product is discharged through a belt. If the product passes the detection, it is handed over to the subsequent machine or outfed.
Applicable Product Specifications
The OL-PB3000 accommodates LCD dimensions from 100mm×100mm to 380mm×380mm. The FPC & COF (Chip On Film) dimensions range from 20mm×20mm to 80mm×80mm, with a maximum of 6 FPC & COF units on a single edge and a center distance of≥60mm. The PCB length can be 70 – 380mm, width 10 – 60mm, with a maximum of 1 PCB. The maximum finished product size is 480mm. The ACF can be of the reel type, with 2 or 3 layers. The ACF attachment length is 5 – 80mm, and the width is 0.3 – 5mm, adjustable for different widths. The ACF reel has an inner diameter of 18mm or 25mm, and the maximum reel diameter is 200mm.
Machine Performance Indicators
The OL-PB3000 boasts high-precision production capabilities. The ACF attachment accuracy is X:±0.15mm, Y:±0.1mm. The FOB main pressing accuracy is X: ±25um, Y:±30um. The production cycle is≤10sec/pcs, with the ACF setting time≤0.5sec and the main pressing setting time≤10sec. It is suitable for FOB bonding of single-edge 1 – 6 FPC products. When switching to a new model, the time required is≤90min, and for existing models, it’s≤50min, depending on the engineer’s proficiency.
The temperature control for ACF-bonding ranges from RT (Room Temperature) to 120℃, and for main-bonding, it’s RT to 400℃. The heating method for the pressing head is constant heat, with temperature control via PID (Proportional Integral Derivative) control and touch screen settings. The temperature error on the pressing head surface is±5℃, using K-type thermocouples. The time setting for ACF-bonding is 0.1 – 9.9Sec, and for main-bonding, it’s 0.1 – 99.9Sec. The pressure regulation range for ACF-bonding is 10 – 150N, and for main-bonding, it’s 20 – 600N. Pressure regulation for ACF is via a precision pressure regulator, while for main pressing, it’s controlled by a proportional valve and touch screen adjustments.
Overall Machine Specifications
The machine dimensions are approximately 4400mm (length) ×2000mm (width) ×1900mm (height), with a working height of 1000mm. It weighs around 3000KG and comes in ivory white. It requires a cleanroom environment of class 1000 or below. The power supply is three-phase 380V. The machine has a maximum power of 15KW. The air source requirement is a clean compressed air of≥0.5 – 0.7MPa, with a consumption of≈200L/min. The machine is equipped with a vacuum pump (200L/min) and a storage tank. It also features an exhaust system with a centralized silencer. For safety, it has an emergency stop button with a protective cover, interlocking design, and alarm systems.
The PCB loading section uses tray loading with a tray size range of 400x500mm (max) and 250x250mm (min), and a maximum stack height of 400mm.
The FOG loading can be via belt, platform, or upstream machine integration, with offline unloading. The outfeeding section can directly connect with downstream machines.
The FOG mechanical hands are equipped with vacuum groups and quantity selectable according to product dimensions, with vacuum value digital displays.
The X-axis is driven by linear motor, θ-axis by servo + harmonic reducer, and Z-axis by slide cylinder lifting.
The ACF unit features automatic semi-cutting, with cutting depth adjustable via a micrometer.
The ACF stage includes platform vacuum, material, and flatness specifications.
The ACF detection part uses a CCD vision system.
The pre-main pressing unit has 4 pressing heads per group, driven by servo + cylinder + guide rail.
The pre-main pressing stage involves Y1-axis, X-axis, Y2-axis, FOG-Z-axis, and PCB-Z-axis movements, all driven by servo motors.
The pre-main pressing alignment CCD uses linear motor + guide rail for X-axis movement.
The main pressing backup part has specific material, size, and surface flatness requirements.
The buffer material supply part involves step motor-driven rotation, manual width adjustment, and sensor detection for material exhaustion.
The image processing unit employs the Boss system with multiple CCD cameras, same-axis light barrels, and different magnifications and field of views for various detection parts. The control unit uses PLC control with a touch screen interface supporting manual and automatic modes. It displays working parameters and can store data for 100 varieties. It also has emergency stop buttons, power switches, lighting switches, door interlock functions, and a three-color operation indicator light.
File Documentation and After-sales Service
The company provides an operation manual and offers training on equipment installation, operation, calibration, parameter setting, maintenance, and troubleshooting. It also includes one year of free after-sales service (excluding damages caused by human error) and lifelong technical support.
Major Component Brands
The OL-PB3000 utilizes high-quality components from renowned brands, such as Servo motors from Rite,丝杆 from THK and 上银, DDR from雅克贝斯,导轨 from THK and 上银, pneumatic elements from SMC and 亚德客, PLC from Keyence, touch screens from Weilin, sensors from Meiji, switch power supplies from Mingwei, circuit breakers and contactors from Schneider and 士林, and drag chains from igus.
In summary, the OL-FB3000 Automatic FOB Bonder is a high-precision, efficient, and reliable device designed to meet the stringent requirements of LCD product manufacturing. With its advanced technology, robust performance, and comprehensive after-sales service, it is an ideal choice for businesses in the electronics manufacturing industry seeking to enhance production efficiency and product quality.
COP (Chip On Plastic) and FOP (Film On Plastic) Bonding Machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment used in the electronics industry, particularly for the production of flexible displays and advanced electronic devices. This machine combines the processes of COP and FOP bonding into a single, integrated system, streamlining the manufacturing process and improving efficiency. COP FOP bonding machines are essential for bonding integrated circuits (ICs) and flexible printed circuits (FPCs) to plastic substrates, ensuring high precision and reliability in display manufacturing.
COP FOP Bonding Machines can be classified based on their level of automation and specific applications:
COP FOP Bonding Machines are indispensable across diverse industries:
The electronics industry is continuously evolving, with manufacturers focusing on improving the precision and speed of bonding machines. Future trends include:
COP FOP Bonding Machines are critical components in modern electronics manufacturing, providing a reliable and efficient solution for bonding processes in the production of high-quality displays and electronic devices. They are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial and medical devices, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of quality and performance. With the increasing demand for thinner, lighter, and more durable devices, COP FOP technology continues to play a crucial role in the electronics industry.
Flex cable bonding machines are essential in the manufacturing of electronic devices, particularly for attaching flexible printed circuits (FPCs) or flexible flat cables (FFCs) to various substrates. These machines ensure a seamless and robust connection between the flexible cable and the electronic components, playing a crucial role in the production of devices like smartphones, tablets, and automotive displays.
Flex cable bonding machines can be classified based on their specific applications and the type of bonding process they perform:
Flex cable bonding machines are indispensable across diverse industries:
The electronics industry is continuously evolving, with manufacturers focusing on improving the precision and speed of bonding machines. Future trends include:
Flex cable bonding machines are critical components in modern electronics manufacturing, providing a reliable and efficient solution for bonding processes in the production of high-quality displays and electronic devices. They are used in a wide range of applications, from consumer electronics to industrial and medical devices, ensuring that products meet the highest standards of quality and performance. With the increasing demand for thinner, lighter, and more durable devices, flex cable bonding technology continues to play a crucial role in the electronics industry.
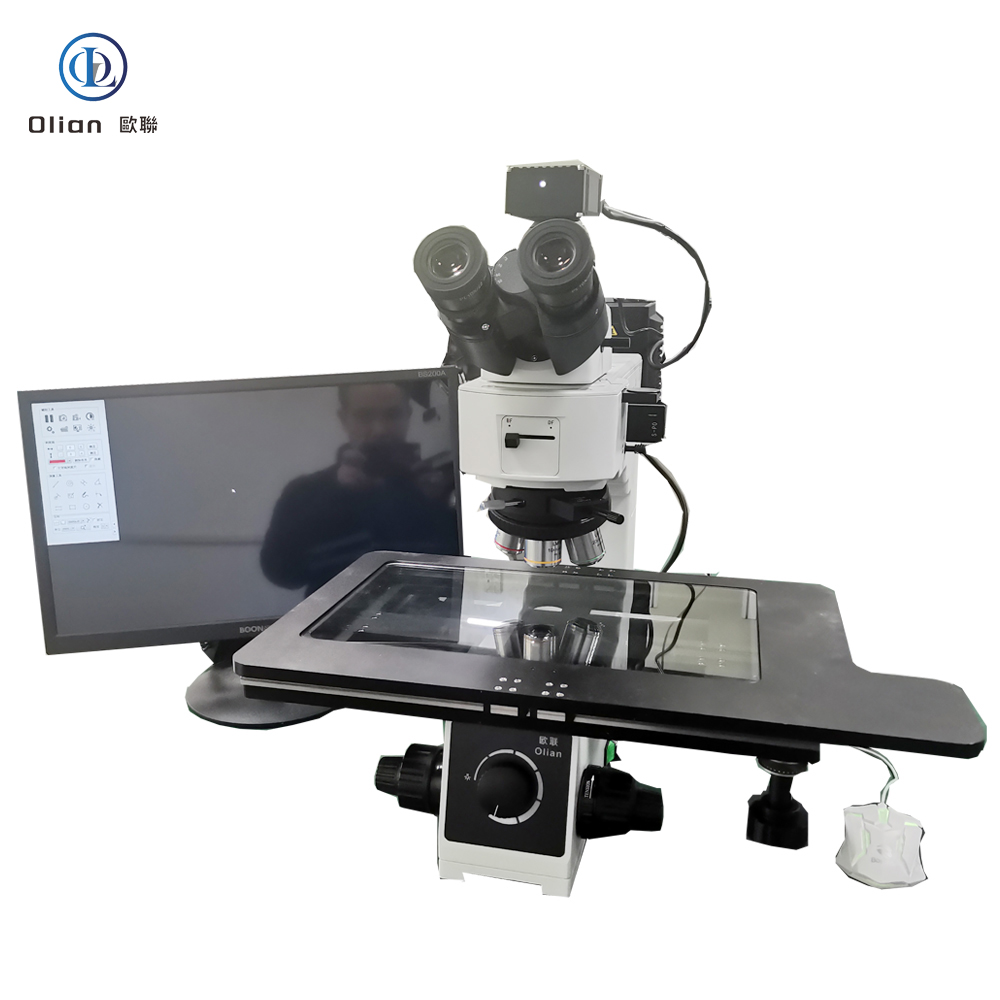

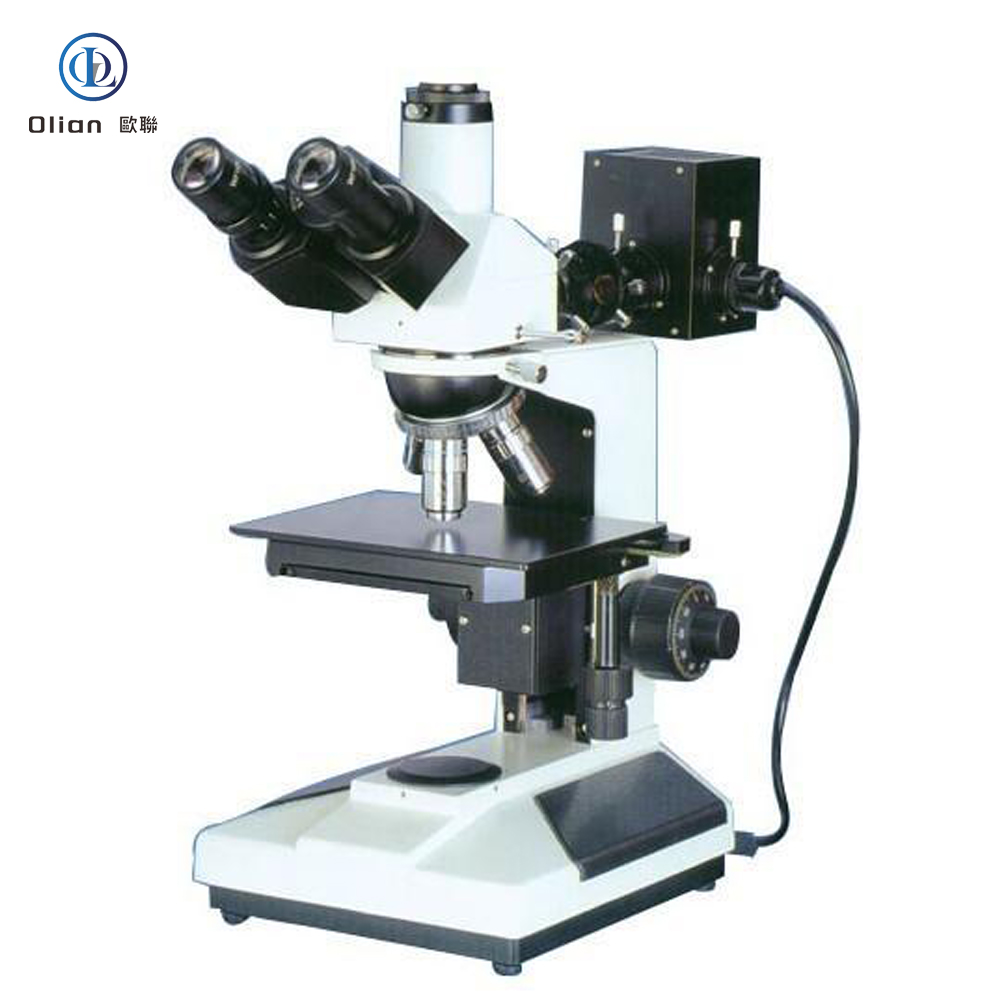
In the electronics manufacturing industry, particularly in the ACF (Anisotropic Conductive Film) bonding process, a variety of testing machines and equipment are essential to ensure the quality and reliability of the final products. These machines play a crucial role in the production line, from initial material inspection to final product testing. Here is a comprehensive overview of the testing instruments and equipment used in ACF bonding processes:
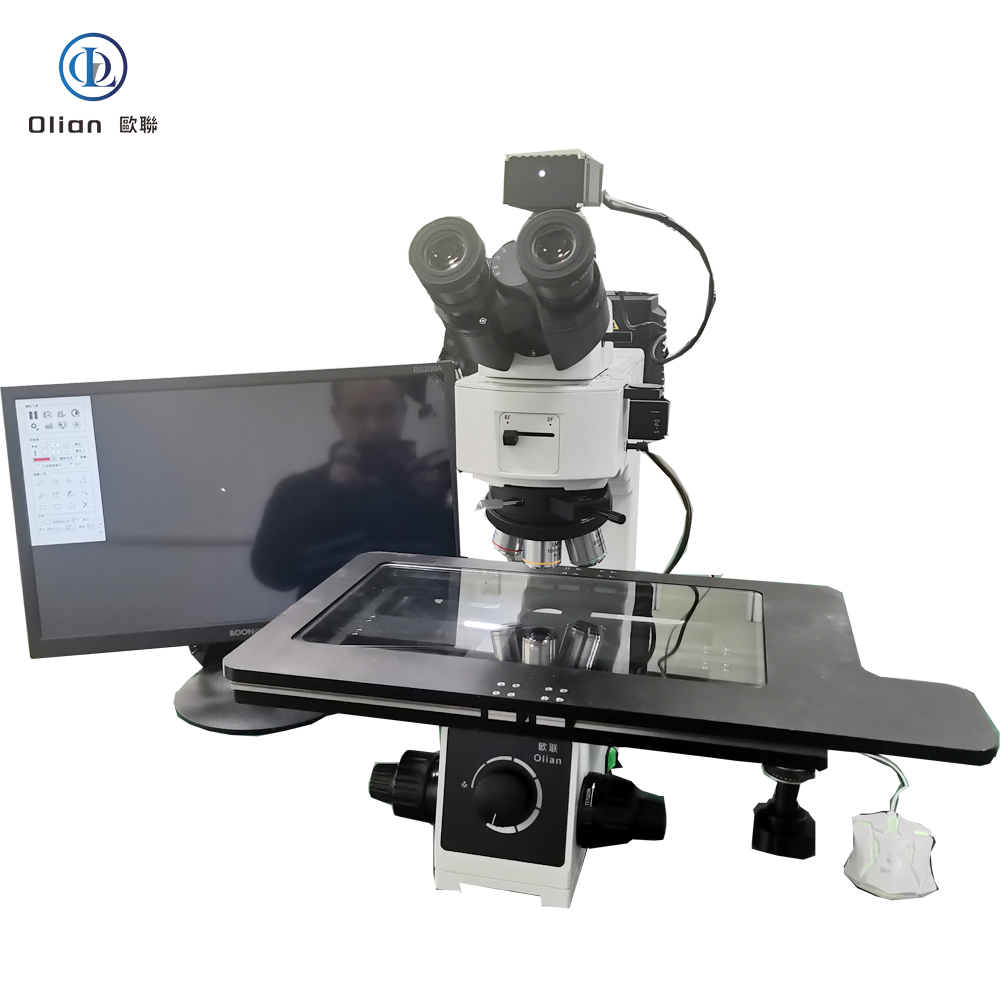
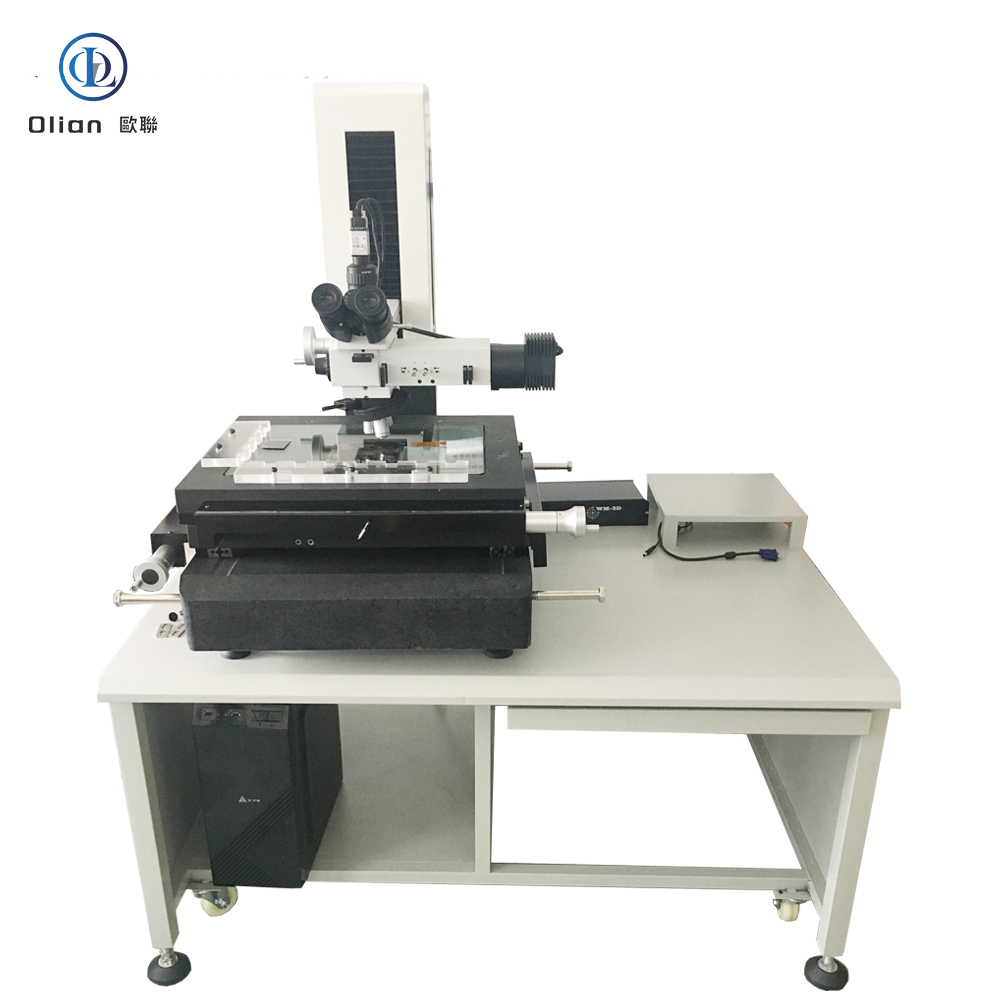
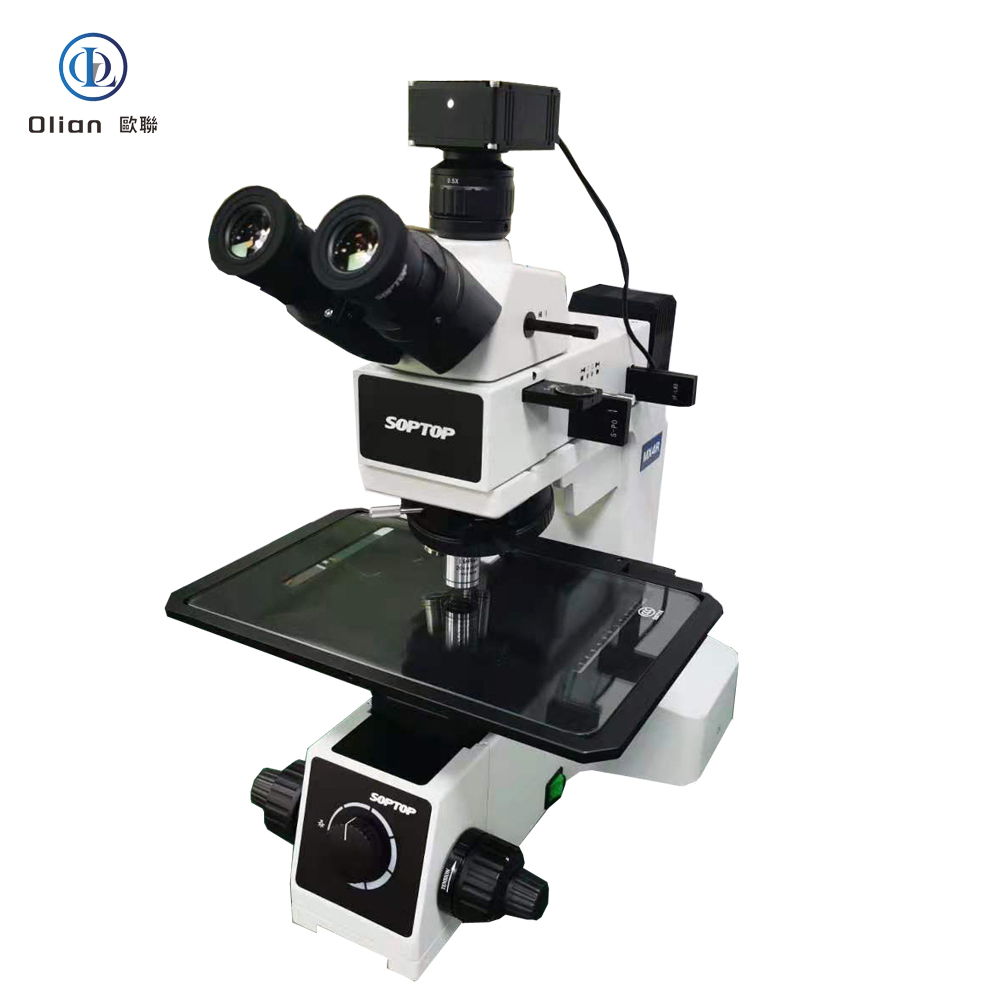
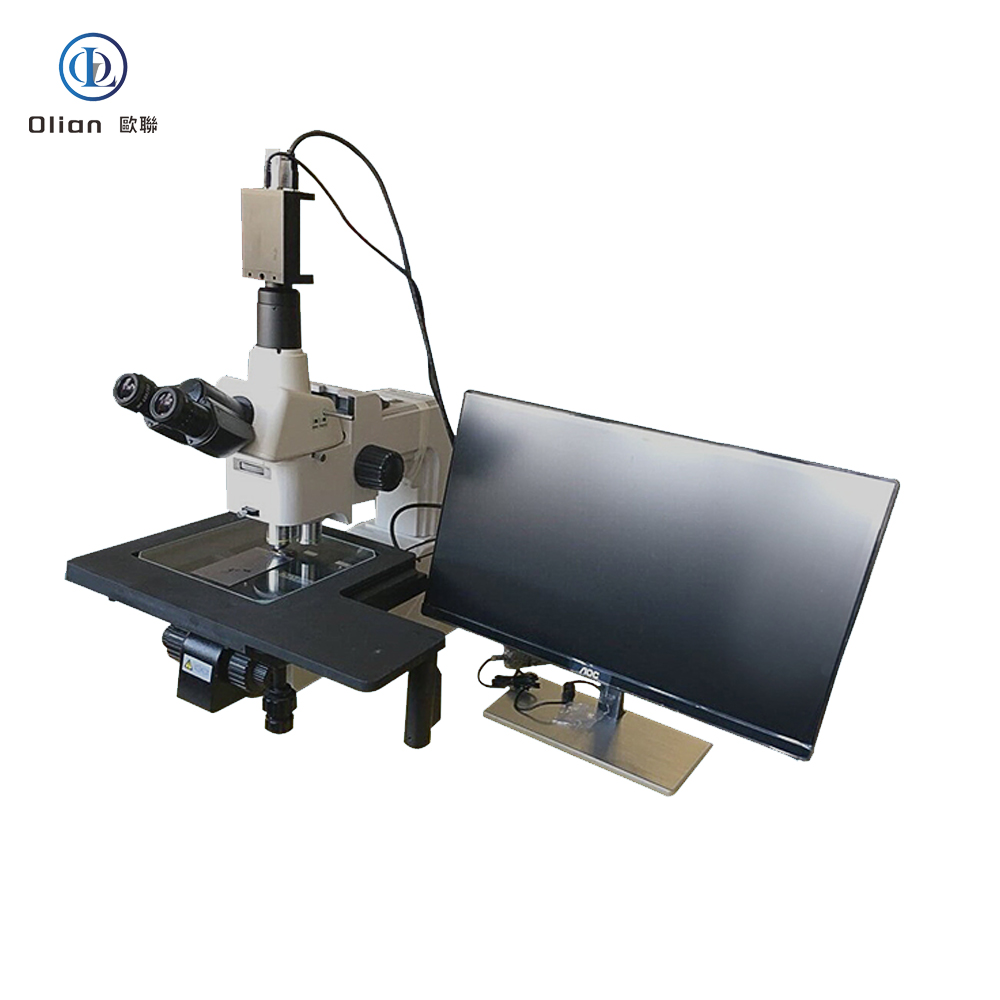
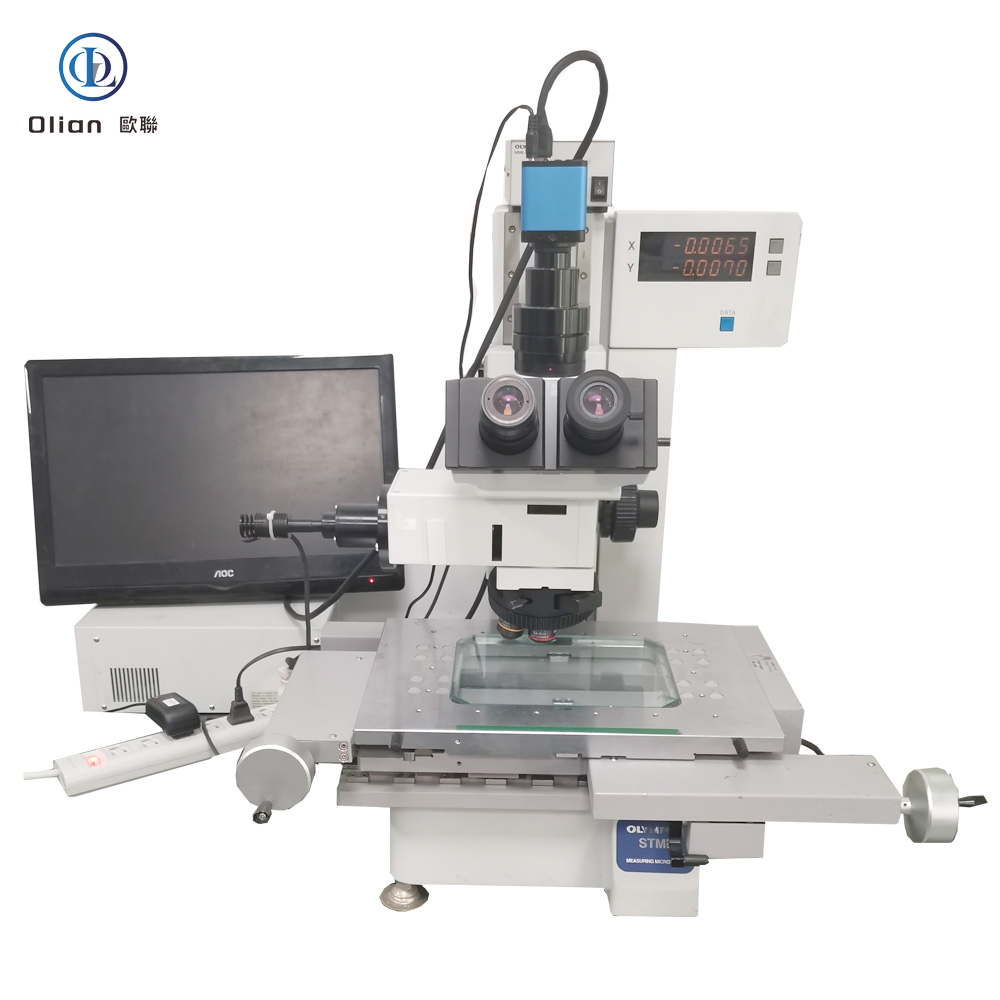
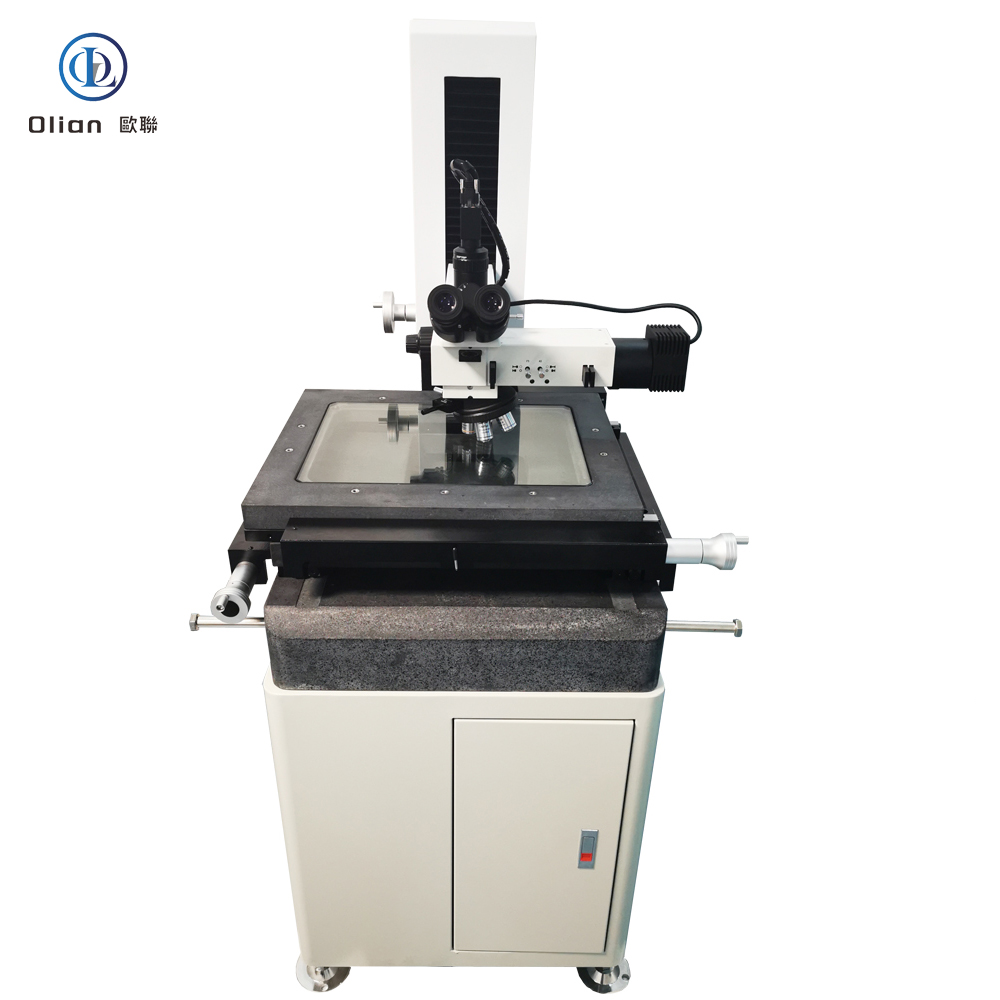
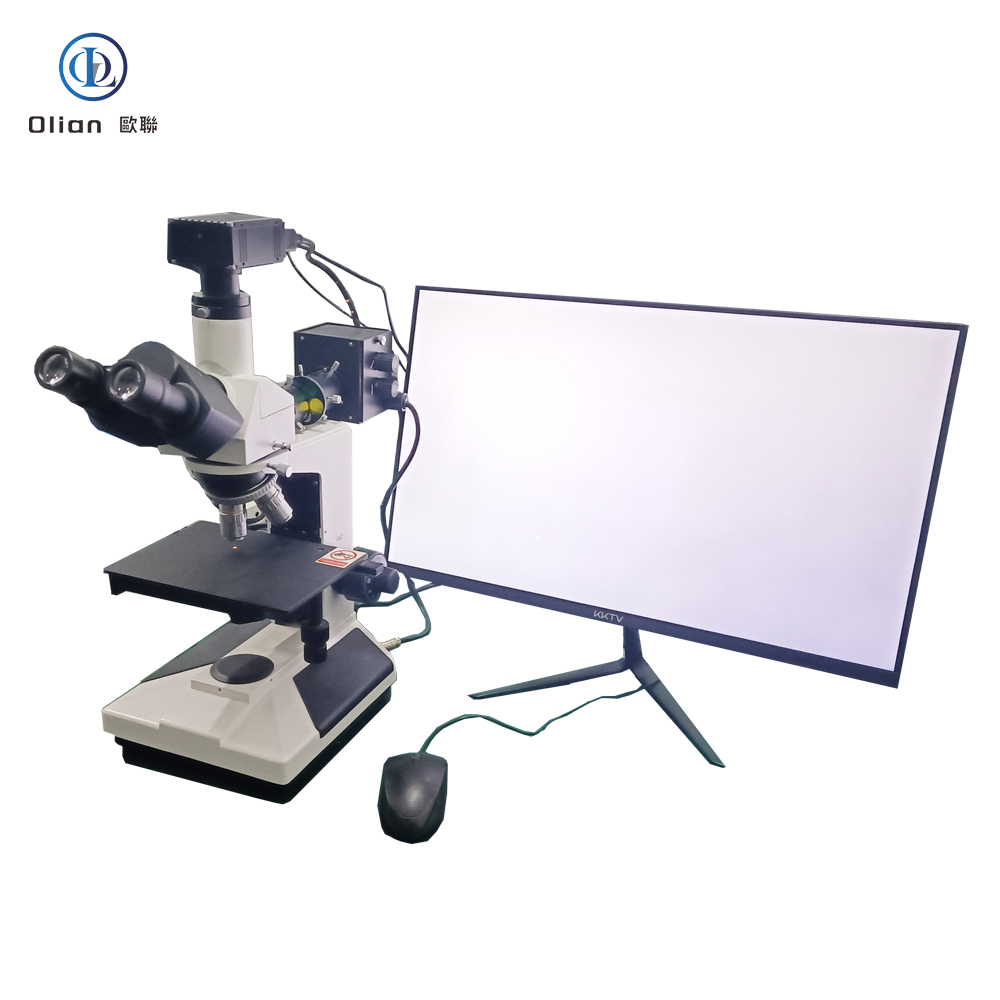
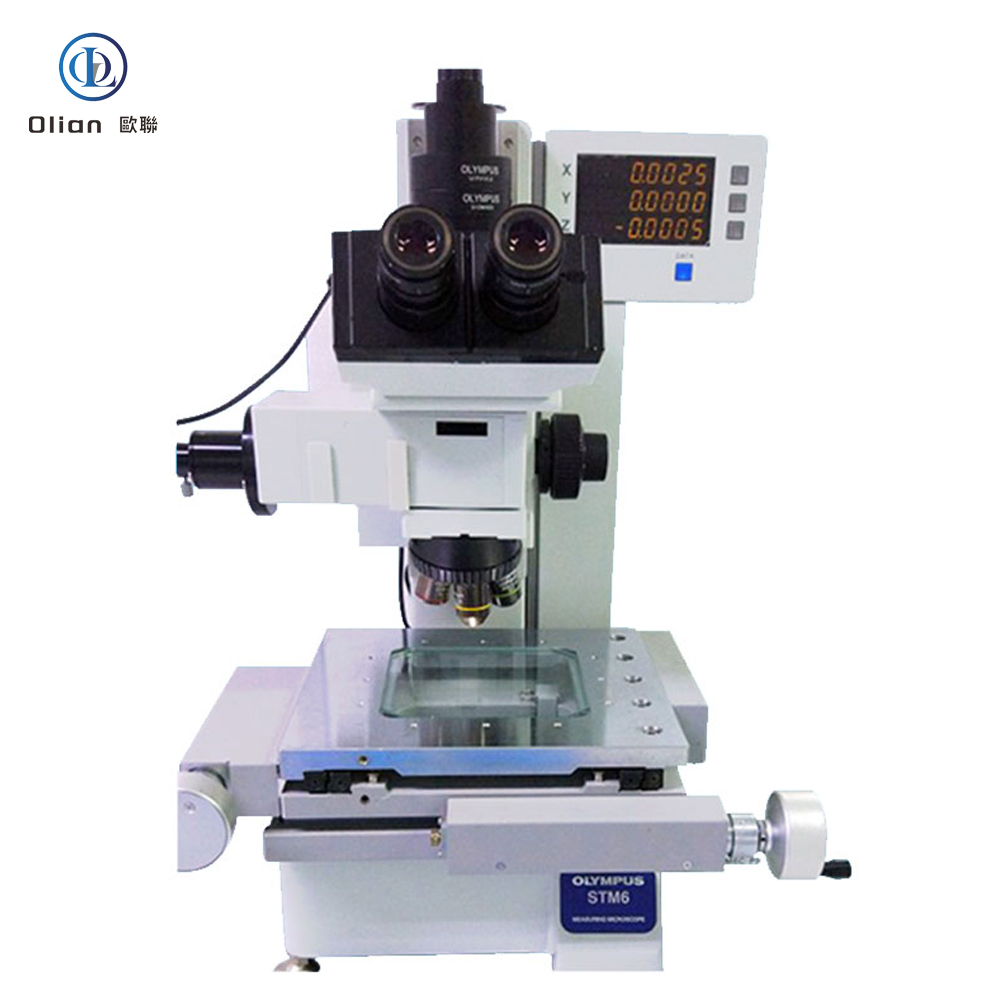









Interferometer Microscope: Interferometer microscopes are used to analyze the surface topography of materials with high precision. They are essential for inspecting the quality of ACF and the bonding surfaces of components. By using optical interference, these microscopes can detect minute surface irregularities that might affect the bonding process.
Metallographic Microscope: Metallographic microscopes are designed to examine the microstructure of metals and alloys. In the context of ACF bonding, they are used to analyze the metallurgical properties of the bonding sites. This helps in understanding the compatibility of the materials and the effectiveness of the bonding process.
Lens Inspection Microscope: Lens inspection microscopes are used to inspect and analyze optical components, such as the lenses used in display devices. They ensure that the optical properties of the components are maintained after the bonding process. High-resolution imaging helps in detecting any defects that might have occurred during bonding.
Tool Microscope: Tool microscopes are used for measuring and inspecting the dimensions and geometry of tools and mechanical parts. In ACF bonding, they are used to verify the alignment and precision of the bonding equipment. This ensures that the bonding process is accurate and consistent.













Temperature Testing Instrument: Temperature testing instruments are crucial for monitoring and controlling the temperature during the ACF bonding process. They ensure that the bonding temperature is maintained within the specified range, which is critical for the quality of the bond. These instruments can be contact or non-contact types, providing real-time temperature data.
Temperature Curve Testing Instrument: Temperature curve testing instruments measure and record temperature changes over time. They are used to analyze the thermal behavior of the bonding process and to optimize the temperature profile. This helps in achieving a consistent and reliable bond quality.
Pressure Testing Device: Pressure testing devices are used to measure and control the pressure applied during the ACF bonding process. They ensure that the pressure is uniform and within the specified limits, which is essential for a strong and durable bond. These devices can handle a wide range of pressures and provide precise control.
Tensile Testing Machine: Tensile testing machines are used to measure the tensile strength of the bonds created by the ACF process. They apply tensile force to the bonded components and measure the response. This helps in determining the mechanical strength of the bonds and ensuring that they can withstand the required forces.
High Temperature High Humidity Testing Chamber: These chambers simulate high temperature and high humidity conditions to test the adaptability and reliability of the bonded products. They are used to evaluate the long-term performance of the products under extreme environmental conditions.
Cold Hot Shock Testing Chamber: Cold hot shock testing chambers rapidly change the temperature to simulate extreme temperature variations. They are used to test the thermal shock resistance of the bonded products, ensuring that they can withstand rapid temperature changes without failure.
Salt Spray Testing Chamber: Salt spray testing chambers simulate a corrosive environment to test the corrosion resistance of the bonded products. This is particularly important for products that will be used in harsh environments, such as automotive and marine applications.
2D Measuring Instrument: 2D measuring instruments use optical imaging and image processing to measure two-dimensional dimensions with high precision. They are used to verify the dimensional accuracy of the components before and after the bonding process. This ensures that the components meet the required specifications.
Contact Angle Meter: Contact angle meters measure the contact angle of a liquid on a solid surface, providing information about surface wettability and adhesion. In ACF bonding, they are used to evaluate the surface properties of the bonding sites, ensuring that the ACF can adhere properly.
Drop Tester: Drop testers simulate the impact of dropping products to test their durability and shock resistance. They are used to ensure that the bonded products can withstand accidental drops during handling and transportation.
Vibration Testing Machine: Vibration testing machines simulate various vibration conditions to test the vibration resistance and reliability of the bonded products. They are used to ensure that the products can operate reliably in vibrating environments, such as in automotive and aerospace applications.
IC Disassembly Machine: IC disassembly machines are used to carefully remove integrated circuits (ICs) from their substrates without causing damage. This is crucial for repair and rework processes in the electronics industry.
IC Removal Machine: IC removal machines are designed to safely and efficiently remove ICs from printed circuit boards (PCBs). They are essential for maintaining the integrity of the board and the components during the repair process.
ACF Cutting Machine: ACF cutting machines are used to cut the ACF tape to the required length and shape. These machines ensure that the ACF tape is accurately cut and positioned for the bonding process.
ACF Bonding Machine: ACF bonding machines are used to bond the ACF tape to the substrates (LCD, PCB, Flex, COF, IC Chip, FPC, etc.) using appropriate temperature, pressure, and time. These machines are available in various configurations, including constant heat systems and pulse heat systems, to meet different bonding requirements.
ACF Pre-Bonding Machine: ACF pre-bonding machines are used to pre-bond ICs or COF on the panel that has been attached to the ACF. The pick and place of the panel is achieved manually, and the pre-alignment is automatically completed by the equipment.
ACF Final Bonding Machine: ACF final bonding machines perform the main bonding on the LCD glass with IC, cable, or COF pre-pressed. The operator manually loads and unloads the products, while the ACF bonding is automatically performed by the machine.
Top-Bottom Alignment Bonding Machine: Top-bottom alignment bonding machines are used to bond FPC/Zebra paper on the PCB/Glass with the ACF attached. The pick and place and alignment of the PCB/Panel are done manually, and the ACF bonding is done automatically. These machines are suitable for 1″ to 12″ flat glass and flexible screen products bonding.
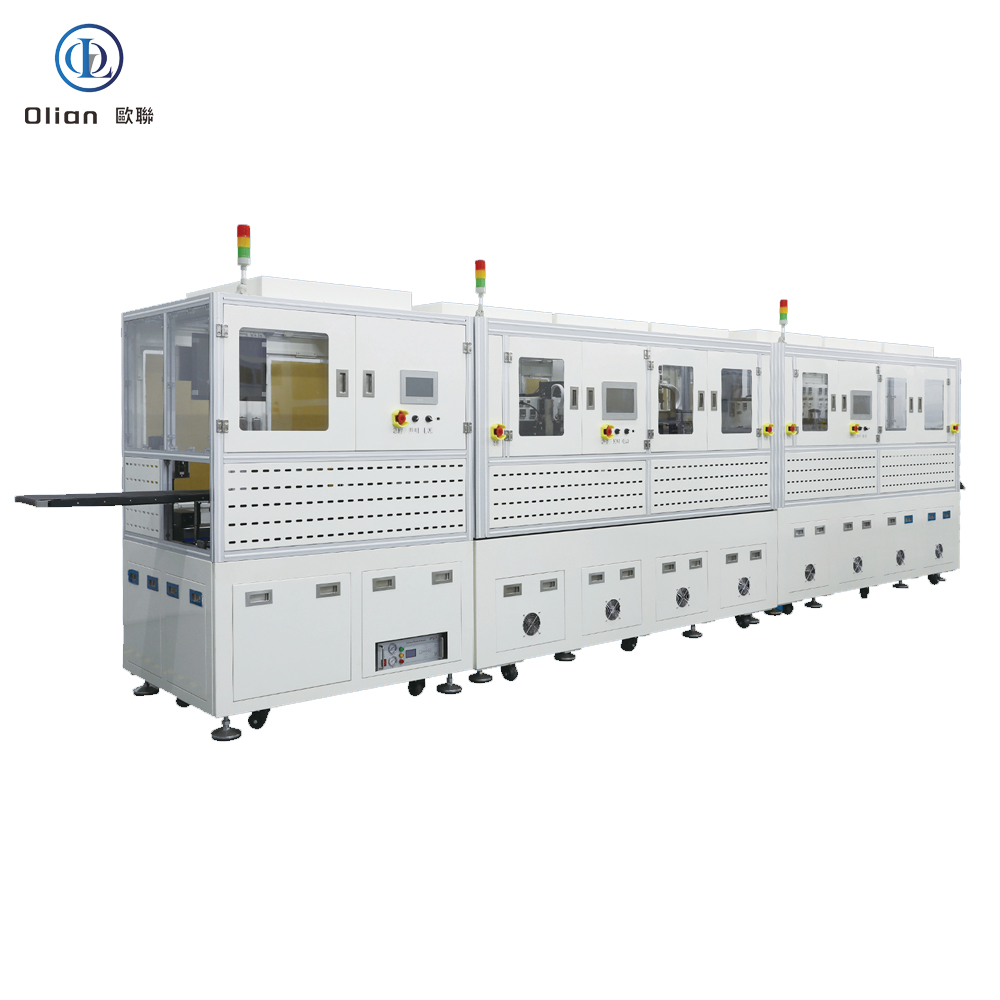
A fully automatic ACF bonding line includes multiple machines working together to automate the entire bonding process. This includes substrates loading machines, terminal cleaning machines, fully automatic COG/COF/COP bonding machines, and fully automatic COF punching machines.
In conclusion, the ACF bonding process relies on a suite of sophisticated testing machines and equipment to ensure the quality and reliability of the final products. Each type of testing equipment plays a critical role in different stages of the production process, from initial material inspection to final product testing. By using these machines, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce defects, and ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
In the ACF (Anisotropic Conductive Film) bonding process, a variety of parts and accessories are used to ensure the quality and reliability of the final products. These components play a crucial role in the production line, from initial material preparation to final product testing. Here is a comprehensive overview of the parts and accessories used in ACF bonding processes:






ACF Tape is the core material used in the ACF bonding process. It is an epoxy adhesive system filled with conductive particles that provide electrical interconnection between pads through the film thickness (z-direction). The conductive particles are distributed far apart to ensure electrical insulation in the plane direction (X&Y) of the film. ACF tape is available in various models and is specific to the application for which it is designed. For example, ACF designed for flex-on-glass (FOG) assembly is usually not suitable for chip-on-glass (COG) or chip-on-film (COF) applications.
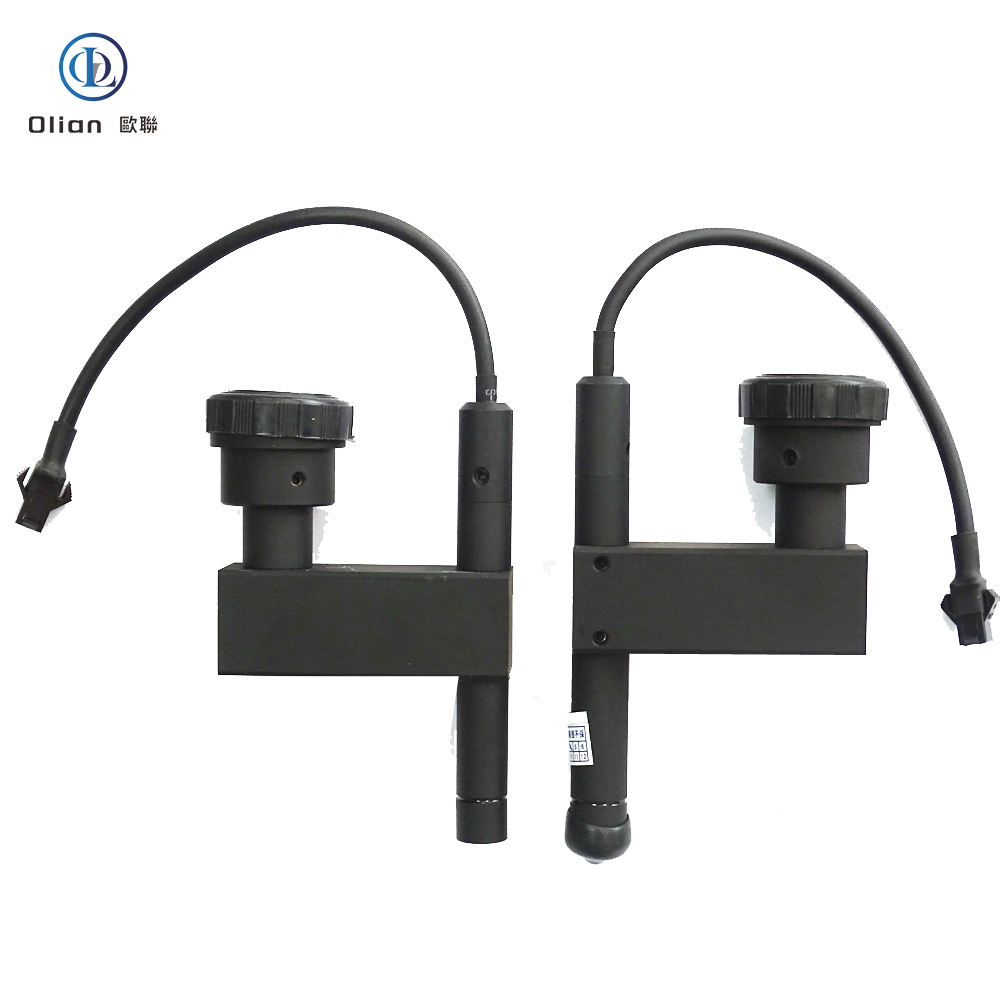
The Hot Bar or Thermode is the primary tool used to apply heat and pressure during the ACF bonding process. Hot bar bonding systems are designed to heat the hot bar to a specific temperature using low voltage electricity, which temperature is fed back to the controller via a thermocouple. The hot bar is brought into contact with the ACF film over the bonding pad, heated to the bonding temperature, and held for a specified time. This process produces the connection between the ACF tape and the components.
Bonding Heads are designed to hold the components and position the ACF tape correctly with the conductive pads on the PCB or other components. They ensure that the bonding process is accurate and consistent. Bonding heads can be manual or automated, depending on the specific requirements of the bonding process.
ACF Cutting Machines are used to cut the ACF tape to the required length and shape. These machines ensure that the ACF tape is accurately cut and positioned for the bonding process. The cutting is done using the half-cut method, where only the actual ACF material is cut, and the cover-layer is used for tape transport.
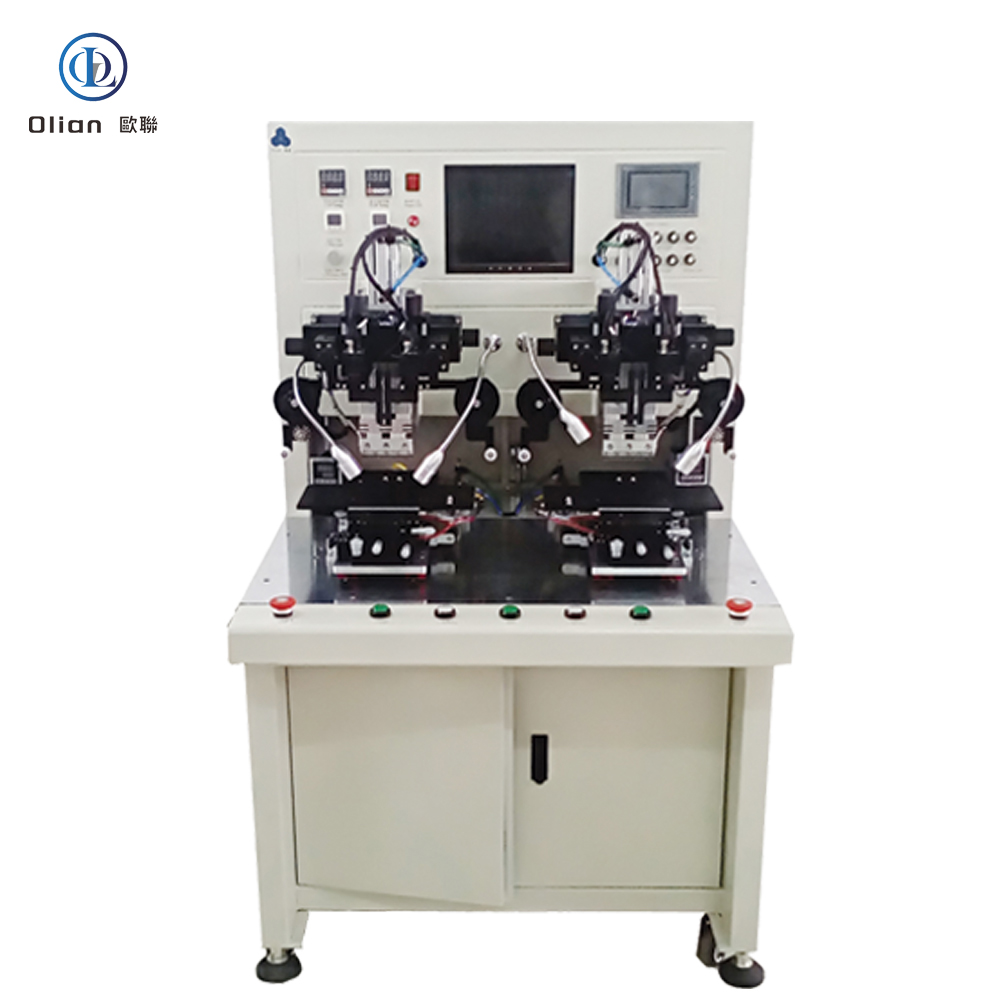
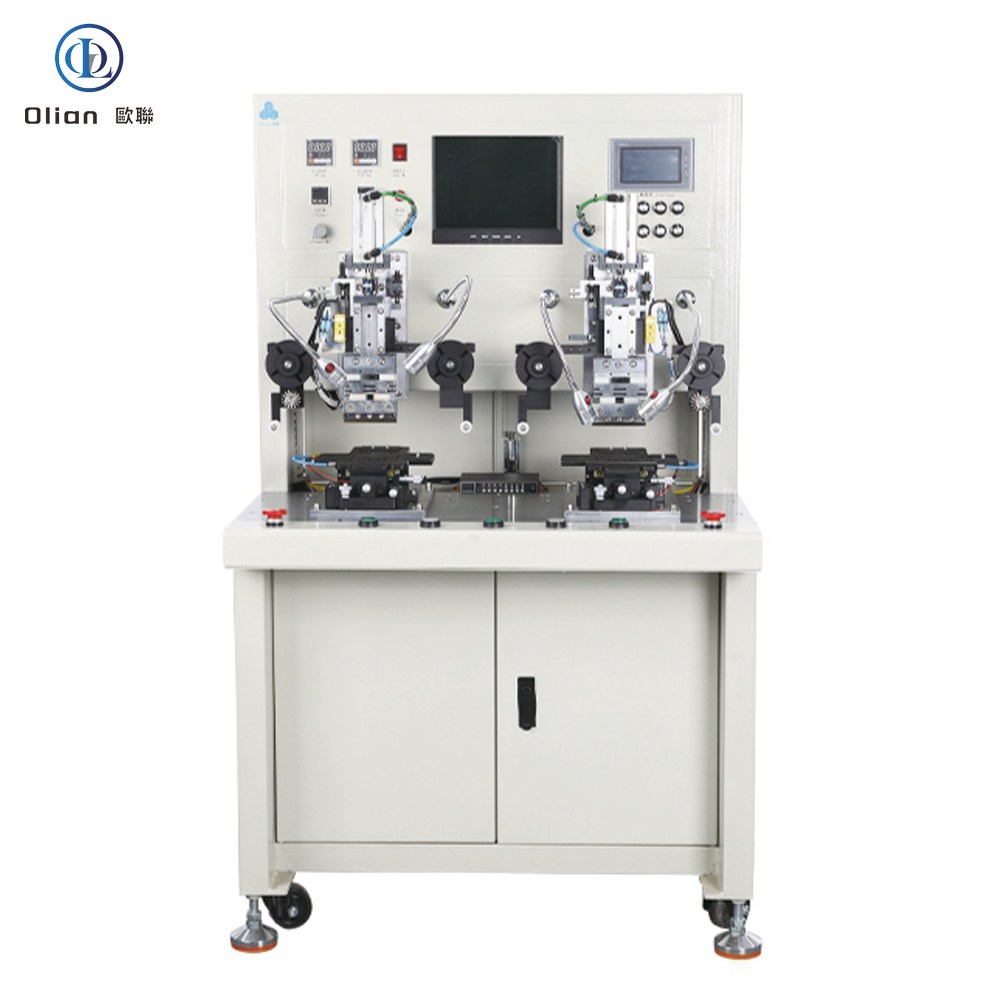
Pre-Bonding Machines are used to pre-bond ICs or COF on the panel that has been attached to the ACF. The pick and place of the panel is achieved manually, and the pre-alignment is automatically completed by the equipment.
Final Bonding Machines perform the main bonding on the LCD glass with IC, cable, or COF pre-pressed. The operator manually loads and unloads the products, while the ACF bonding is automatically performed by the machine.
Top-Bottom Alignment Bonding Machines are used to bond FPC/Zebra paper on the PCB/Glass with the ACF attached. The pick and place and alignment of the PCB/Panel are done manually, and the ACF bonding is done automatically. These machines are suitable for 1″ to 12″ flat glass and flexible screen products bonding.
A Fully Automatic ACF Bonding Line includes multiple machines working together to automate the entire bonding process. This includes substrates loading machines, terminal cleaning machines, fully automatic COG/COF/COP bonding machines, and fully automatic COF punching machines.
Testing and Inspection Equipment is used to ensure the quality and reliability of the bonded products. This includes microscopes for surface inspection, temperature and pressure testers, and environmental testing chambers to simulate various conditions.
ACF bonding is widely used in various industries, including mobile phone manufacturing, automotive, LCD production, mobile computers, TV manufacturing, open cell panels, touch panels, smart watches, and pads. It is also used in research labs focusing on LCD/LED/OLED/MICRO LED/MINI LED displays.
ACF bonding offers several benefits, including:
In conclusion, the ACF bonding process relies on a suite of sophisticated parts and accessories to ensure the quality and reliability of the final products. Each component plays a critical role in different stages of the production process, from initial material preparation to final product testing. By using these parts and accessories, manufacturers can optimize their processes, reduce defects, and ensure that their products meet the highest standards of quality and performance.